Unsaturated Fatty Acids Affect Quorum Sensing Communication System and Inhibit Motility and Biofilm Formation of Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 29320462
- PMCID: PMC5796163
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19010214
Unsaturated Fatty Acids Affect Quorum Sensing Communication System and Inhibit Motility and Biofilm Formation of Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
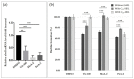
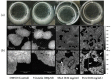
The increasing threat of Acinetobacter baumannii as a nosocomial pathogen is mainly due to the occurrence of multidrug-resistant strains that are associated with the real problem of its eradication from hospital wards. The particular ability of this pathogen to form biofilms contributes to its persistence, increases antibiotic resistance, and promotes persistent/device-related infections. We previously demonstrated that virstatin, which is a small organic compound known to decrease virulence of Vibrio cholera via an inhibition of T4-pili expression, displayed very promising activity to prevent A. baumannii biofilm development. Here, we examined the antibiofilm activity of mono-unsaturated chain fatty acids, palmitoleic (PoA), and myristoleic (MoA) acids, presenting similar action on V. cholerae virulence. We demonstrated that PoA and MoA (at 0.02 mg/mL) were able to decrease A. baumannii ATCC 17978 biofilm formation up to 38% and 24%, respectively, presented a biofilm dispersing effect and drastically reduced motility. We highlighted that these fatty acids decreased the expression of the regulator abaR from the LuxIR-type quorum sensing (QS) communication system AbaIR and consequently reduced the N-acyl-homoserine lactone production (AHL). This effect can be countered by addition of exogenous AHLs. Besides, fatty acids may have additional non-targeted effects, independent from QS. Atomic force microscopy experiments probed indeed that PoA and MoA could also act on the initial adhesion process in modifying the material interface properties. Evaluation of fatty acids effect on 22 clinical isolates showed a strain-dependent antibiofilm activity, which was not correlated to hydrophobicity or pellicle formation ability of the tested strains, and suggested a real diversity in cell-to-cell communication systems involved in A. baumannii biofilm formation.
Keywords: biofilm; myristoleic acid; palmitoleic acid; pellicle; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quorum-sensing system in Acinetobacter baumannii: a potential target for new drug development.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jan;128(1):15-27. doi: 10.1111/jam.14330. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31102552 Review.
-
Multiple Quorum Quenching Enzymes Are Active in the Nosocomial Pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC17978.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Sep 13;8:310. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00310. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30271754 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Polymyxin B in Combination with Ceftazidime against Robust Biofilm Formed by Acinetobacter baumannii with Genetic Deficiency in AbaI/AbaR Quorum Sensing.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0176821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01768-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196792 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing pili assembly and biofilm formation in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC19606 using non-native acyl-homoserine lactones.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Mar 7;15:62. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0397-5. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25888221 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in Acinetobacter: an emerging pathogen.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010 Nov;36(4):349-60. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2010.512269. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20846031 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrolysis of Edible Oils by Fungal Lipases: An Effective Tool to Produce Bioactive Extracts with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potential.Foods. 2022 Jun 10;11(12):1711. doi: 10.3390/foods11121711. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35741908 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Holy Triangle of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 16;10(6):1239. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061239. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting microbial quorum sensing: the next frontier to hinder bacterial driven gastrointestinal infections.Gut Microbes. 2023 Dec;15(2):2252780. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2252780. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37680117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanocarriers-Enabled Delivery of Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Adjuvants to Overcome Bacterial Biofilms.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 14;16(3):396. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030396. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling in Acinetobacter baumannii: Quorum sensing and nucleotide second messengers.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 May 22;27:2168-2175. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.032. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40510767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee C.-R., Lee J.H., Park M., Park K.S., Bae I.K., Kim Y.B., Cha C.-J., Jeong B.C., Lee S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms, and Prospective Treatment Options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017;7:55. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

