Longitudinal micro-CT as an outcome measure of interstitial lung disease in TNF-transgenic mice
- PMID: 29320550
- PMCID: PMC5761871
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190678
Longitudinal micro-CT as an outcome measure of interstitial lung disease in TNF-transgenic mice
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a debilitating condition with poor survival prognosis. High resolution computed tomography (CT) is a common clinical tool to diagnose RA-ILD, and is increasingly being adopted in pre-clinical studies. However, murine models recapitulating RA-ILD are lacking, and CT outcomes for inflammatory lung disease have yet to be formally validated. To address this, we validate μCT outcomes for ILD in the tumor necrosis factor transgenic (TNF-Tg) mouse model of RA.
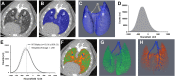
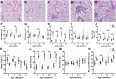
Methods: Cross sectional μCT was performed on cohorts of male TNF-Tg mice and their WT littermates at 3, 4, 5.5 and 12 months of age (n = 4-6). Lung μCT outcomes measures were determined by segmentation of the μCT datasets to generate Aerated and Tissue volumes. After each scan, lungs were obtained for histopathology and 3 sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Automated histomorphometry was performed to quantify the tissue area (nuclei, cytoplasm, and extracellular matrix) and aerated area (white space) within the tissue sections. Spearman's correlation coefficients were used to evaluate the extent of association between μCT imaging and histopathology endpoints.
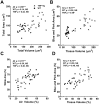
Results: TNF-Tg mice had significantly greater tissue volume, total lung volume and mean intensity at all timepoints compared to age matched WT littermates. Histomorphometry also demonstrated a significant increase in tissue area at 3, 4, and 5.5 months of age in TNF-Tg mice. Lung tissue volume was correlated with lung tissue area (ρ = 0.81, p<0.0001), and normalize lung aerated volume was correlated with normalized lung air area (ρ = 0.73, p<0.0001).
Conclusions: We have validated in vivo μCT as a quantitative biomarker of ILD in mice. Further, development of longitudinal measures is critical for dissecting pathologic progression of ILD, and μCT is a useful non-invasive method to study lung inflammation in the TNF-Tg mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF, Achenbach SJ, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, et al. Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(6):1583–91. doi: 10.1002/art.27405 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doyle JJ, Eliasson AH, Argyros GJ, Dennis GJ, Finger DR, Hurwitz KM, et al. Prevalence of pulmonary disorders in patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19(3):217–21. - PubMed
-
- Kim EJ, Elicker BM, Maldonado F, Webb WR, Ryu JH, Van Uden JH, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2010;35(6):1322–8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00092309 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaw M, Collins BF, Ho LA, Raghu G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(135):1–16. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00008014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(6):788–824. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

