High AHR expression in breast tumors correlates with expression of genes from several signaling pathways namely inflammation and endogenous tryptophan metabolism
- PMID: 29320557
- PMCID: PMC5761880
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190619
High AHR expression in breast tumors correlates with expression of genes from several signaling pathways namely inflammation and endogenous tryptophan metabolism
Abstract
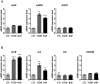
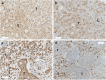
Increasing epidemiological and animal experimental data provide substantial support for the role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in mammary tumorigenesis. The effects of AhR have been clearly demonstrated in rodent models of breast carcinogenesis and in several established human breast cancer cell lines following exposure to AhR ligands or AhR overexpression. However, relatively little is known about the role of AhR in human breast cancers. AhR has always been considered to be a regulator of toxic and carcinogenic responses to environmental contaminants such as TCDD (dioxin) and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP). The aim of this study was to identify the type of breast tumors (ERα-positive or ERα-negative) that express AHR and how AhR affects human tumorigenesis. The levels of AHR, AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT) and AHR repressor (AHRR) mRNA expression were analyzed in a cohort of 439 breast tumors, demonstrating a weak association between high AHR expression and age greater than fifty years and ERα-negative status, and HR-/ERBB2 breast cancer subtypes. AHRR mRNA expression was associated with metastasis-free survival, while AHR mRNA expression was not. Immunohistochemistry revealed the presence of AhR protein in both tumor cells (nucleus and/or cytoplasm) and the tumor microenvironment (including endothelial cells and lymphocytes). High AHR expression was correlated with high expression of several genes involved in signaling pathways related to inflammation (IL1B, IL6, TNF, IL8 and CXCR4), metabolism (IDO1 and TDO2 from the kynurenine pathway), invasion (MMP1, MMP2 and PLAU), and IGF signaling (IGF2R, IGF1R and TGFB1). Two well-known ligands for AHR (TCDD and BaP) induced mRNA expression of IL1B and IL6 in an ERα-negative breast tumor cell line. The breast cancer ER status likely influences AhR activity involved in these signaling pathways. The mechanisms involved in AhR activation and target gene expression in breast cancers are also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
An Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Amplification Loop That Enforces Cell Migration in ER-/PR-/Her2- Human Breast Cancer Cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;90(5):674-688. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.105361. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Mol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27573671 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor subtype- and promoter-specific modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent transcription.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jun;7(6):977-86. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0396. Epub 2009 May 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19470599
-
A Molecular Mechanism To Switch the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor from a Transcription Factor to an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 15;37(13):e00630-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00630-16. Print 2017 Jul 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28416634 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Estrogen, Kynurenine, and AHR Pathways: An immunosuppressive axis with therapeutic potential for breast cancer treatment.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115804. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115804. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37716620 Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Connects Inflammation to Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 24;21(15):5264. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155264. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Next-generation of BBQ analogues that selectively target breast cancer.Front Chem. 2024 Jun 21;12:1396105. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1396105. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38974991 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in L-Kynurenine-Mediated Parathyroid Hormone-Related Peptide Expression.Horm Cancer. 2019 Jun;10(2-3):89-96. doi: 10.1007/s12672-019-0357-x. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Horm Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30689168 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related increase of kynurenine enhances miR29b-1-5p to decrease both CXCL12 signaling and the epigenetic enzyme Hdac3 in bone marrow stromal cells.Bone Rep. 2020 Apr 23;12:100270. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100270. eCollection 2020 Jun. Bone Rep. 2020. PMID: 32395570 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Development.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 8;12:625346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.625346. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33763068 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor to prevent cancer in barrier organs.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 May;223:116156. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116156. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38518996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Madigan MP, Ziegler RG, Benichou J, Byrne C, Hoover RN. Proportion of breast cancer cases in the United States explained by well-established risk factors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87(22):1681–1685. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M et al. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer—analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(2):78–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200007133430201 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fenton SE, Reed C, Newbold RR. Perinatal environmental exposures affect mammary development, function, and cancer risk in adulthood. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;52:455–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134659 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Phrakonkham P, Brouland JP, Saad Hel S, Bergès R, Pimpie C, Pocard M et al. Dietary exposure in utero and during lactation to a mixture of genistein and an anti-androgen fungicide in a rat mammary carcinogenesis model. Reprod Toxicol. 2015;54:101–109. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.05.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

