Therapeutic Effects of Resiniferatoxin Related with Immunological Responses for Intestinal Inflammation in Trichinellosis
- PMID: 29320813
- PMCID: PMC5776891
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2017.55.6.587
Therapeutic Effects of Resiniferatoxin Related with Immunological Responses for Intestinal Inflammation in Trichinellosis
Abstract
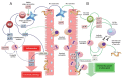
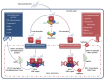
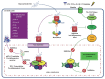
The immune response against Trichinella spiralis at the intestinal level depends on the CD4+ T cells, which can both suppress or promote the inflammatory response through the synthesis of diverse cytokines. During the intestinal phase, the immune response is mixed (Th1/Th2) with the initial predominance of the Th1 response and the subsequent domination of Th2 response, which favor the development of intestinal pathology. In this context, the glucocorticoids (GC) are the pharmacotherapy for the intestinal inflammatory response in trichinellosis. However, its therapeutic use is limited, since studies have shown that treatment with GC suppresses the host immune system, favoring T. spiralis infection. In the search for novel pharmacological strategies that inhibit the Th1 immune response (proinflammatory) and assist the host against T. spiralis infection, recent studies showed that resiniferatoxin (RTX) had anti-inflammatory activity, which decreased the serum levels of IL-12, INF-γ, IL-1β, TNF-α, NO, and PGE2, as well the number of eosinophils in the blood, associated with decreased intestinal pathology and muscle parasite burden. These researches demonstrate that RTX is capable to inhibit the production of Th1 cytokines, contributing to the defense against T. spiralis infection, which places it as a new potential drug modulator of the immune response.
Keywords: Th1 cytokine; Trichinella spiralis; inflammatory response; resiniferatoxin; trichinellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Elliott DE, Summers RW, Weinstock JV. Helminths as governors of immune-mediated inflammation. Int J Parasitol. 2007;37:457–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

