Distribution of glomerular diseases in Taiwan: preliminary report of National Renal Biopsy Registry-publication on behalf of Taiwan Society of Nephrology
- PMID: 29320993
- PMCID: PMC5764016
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0810-4
Distribution of glomerular diseases in Taiwan: preliminary report of National Renal Biopsy Registry-publication on behalf of Taiwan Society of Nephrology
Abstract
Background: Despite the development of biomarkers and noninvasive imaging tools, biopsy remains the only method for correctly diagnosing patients with unexplained hematuria, proteinuria and renal failure. Renal biopsy has been performed for several decades in Taiwan; however, a national data registry is still lacking until 2013.
Methods: The Renal Biopsy Registry Committee was established within the Taiwan Society of Nephrology in January 2013. A biopsy registry format, including basic demographic data, baseline clinical features, laboratory data, and clinical and pathological diagnosis was developed. Approval from the local institutional review board was obtained in each participating medical center.
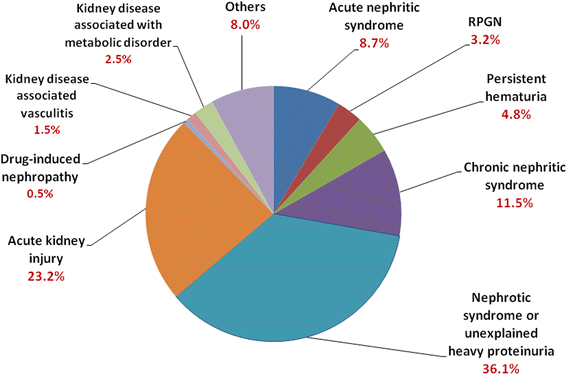
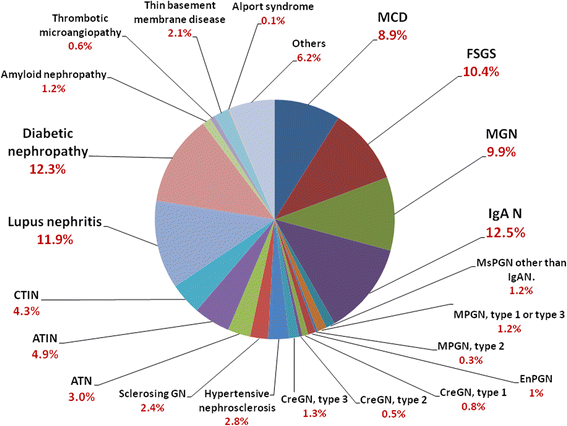
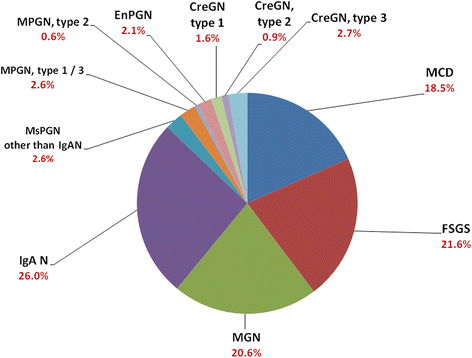
Results: From January 2014 to September 2016, 1445 renal biopsies were identified from 17 medical centers. 53.8% cases were reported in men. After excluding renal transplantation, renal biopsies were commonly performed in patients with primary glomerulonephritis (48.1%), secondary glomerulonephritis (36.2%), followed by tubulointerstitial diseases (12.3%) and vascular nephropathy (3.4%). Among primary glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy (26.0%), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (21.6%), and membranous nephropathy (20.6%) were most frequently diagnosed. Diabetic nephropathy (22.4%) and lupus nephritis (21.8%) were the most common among secondary glomerulonephritis. Patients with minimal change disease and membranous nephropathy had heavier proteinuria than those with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and IgA nephropathy (P < 0.001). Patients with minimal change disease had higher serum IgM and IgE levels. The most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in primary glomerular disease was membranous nephropathy (28.8%), followed by minimal change disease (28.2%). IgA nephropathy was the leading cause of chronic nephritic syndrome, acute nephritic syndrome, and persistent hematuria. The incidence of primary glomerulonephritis was approximately 2.19 in 100,000/year.
Conclusions: This is the first report of the National Renal Biopsy Registry in Taiwan. IgA nephropathy is the most common primary glomerulonephritis, while membranous nephropathy is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome. Primary glomerulonephritis distribution in Taiwan is slightly different from that in other Asian countries.
Keywords: Glomerulonephritis; IgA nephropathy; Renal biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval from the local institutional review board was obtained in each participating medical center. Institutional review boards that approved this study and the ethics approval codes are listed in Additional file 1.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidemiological features of primary glomerular disease in Turkey: a multicenter study by the Turkish Society of Nephrology Glomerular Diseases Working Group.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Nov 14;21(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02134-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33189135 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Experience of Renal Biopsy at a New Nephrology Center in Eastern Nepal.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021 May-Jun;32(3):815-820. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.336778. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021. PMID: 35102925
-
[The incidence of renal diseases as diagnosed by biopsy in Hungary].Orv Hetil. 2004 Jun 27;145(26):1373-9. Orv Hetil. 2004. PMID: 15384747 Hungarian.
-
[Instructions and implementations for percutaneous renal biopsy. Guidelines for the therapy of glomerular nephropaties].G Ital Nefrol. 2003 Sep-Oct;20 Suppl 24:S3-47. G Ital Nefrol. 2003. PMID: 14666502 Review. Italian.
-
Renal pathology in adult and paediatric population of Japan: review of the Japan renal biopsy registry database from 2007 to 2017.J Nephrol. 2023 Nov;36(8):2257-2267. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01687-9. Epub 2023 Aug 19. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37597092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quality Improvement Initiatives in Renal Biopsy for Patient-Centered Communication by Shared Decision Making.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 13;12(5):1227. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051227. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626381 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological features of primary glomerular disease in Turkey: a multicenter study by the Turkish Society of Nephrology Glomerular Diseases Working Group.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Nov 14;21(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02134-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33189135 Free PMC article.
-
[Epidemiology of glomerular disease: report from a third-level center].Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023 Sep 18;61(Suppl 2):S185-S192. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2023. PMID: 38011679 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
The Value of Renal Biopsy in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus in Singapore over the Past Two Decades.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Jul;6(4):284-298. doi: 10.1159/000505624. Epub 2020 May 6. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32923458 Free PMC article.
-
B Cells in Primary Membranous Nephropathy: Escape from Immune Tolerance and Implications for Patient Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13560. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413560. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins AJ, Foley RN, Chavers B, Gilbertson D, Herzog C, Johansen K, Kasiske B, Kutner N, Liu J, St Peter W, et al. 'United States renal data system 2011 annual data report: atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59(1 Suppl 1):A7. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.11.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

