Metformin, Asian ethnicity and risk of prostate cancer in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29320995
- PMCID: PMC5763543
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3934-9
Metformin, Asian ethnicity and risk of prostate cancer in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Metformin is associated with a reduced risk of some cancers but its effect on prostate cancer is unclear. Some studies suggest only Asians derive this benefit. Therefore, we undertook a systematic review with particular attention to ethnicity.
Methods: Medline, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and EBM Reviews were searched from inception to 2015. Two reviewers identified and abstracted articles. Studies were pooled using random effects model and stratified by Western- vs Asian-based populations.
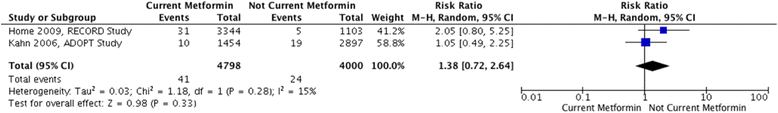
Results: We identified 482 studies; 26 underwent full review. Of Western-based studies (n = 23), two were randomized trials and 21 were observational studies. All Asian-based studies (n = 3) were observational. There were 1,572,307 patients, 1,171,643 Western vs 400,664 Asian. Across all studies there was no association between metformin and prostate cancer (RR: 1.01, 95%CI: 0.86-1.18, I2: 97%), with similar findings in Western-based trials (RR: 1.38, 95%CI: 0.72-2.64 I2: 15%) and observational studies (RR: 1.03 95%CI: 0.94-1.13, I2: 88%). Asian-based studies suggested a non-significant reduction (RR: 0.75, 95%CI: 0.42-1.34, I2: 90%), although these results were highly influenced by one study of almost 400,000 patients (propensity-adjusted RR: 0.47 95%CI 0.45-0.49). Removing this influential study yielded an estimate more congruent with Western-based studies (RR: 0.98 95%CI:0.71-1.36, I2: 0%).
Conclusion: There is likely no association between metformin and risk of prostate cancer, in either Western-based or Asian-based populations after removing a highly influential Asian-based study.
Keywords: Ethnicity & prostate cancer; Metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Bansal D, Bhansali A, Kapil G, Undela K, Tiwari P. Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013;16:151–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical