Psychosocial issues discovered through reflective group dialogue between medical students
- PMID: 29321068
- PMCID: PMC5763939
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-017-1114-x
Psychosocial issues discovered through reflective group dialogue between medical students
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Psychosocial issues discovered through reflective group dialogue between medical students.BMC Med Educ. 2018 Apr 30;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1185-3. BMC Med Educ. 2018. PMID: 29712553 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The biopsychosocial model is a comprehensive approach emphasizing holistic medical care. However, medical curricula that incorporate narrative reflective writing and group dynamic discussion of psychosocial issues among patients and their family members in reflective dialogue groups are currently underutilized. The aim of this study was to determine psychosocial issues among patients and their family members through medical students' reflective dialogue groups.
Methods: This study was completed as part of a pediatric clerkship. Fifty medical students were rotated to the department of Pediatrics. They completed a narrative writing assignment concerning patients' psychosocial issues and participated in a reflective group discussion during the rotation. The recordings of the six reflective group sessions were transcribed for thematic analysis. A six-step theme generation process was conducted in the first reading stage of all transcripts by four researchers. Subsequently, initial codes were generated and potential themes sought before possible themes were reviewed and thematic maps generated. Names for each theme were defined and a scholarly report of the analysis was presented through a consensus-based approach.
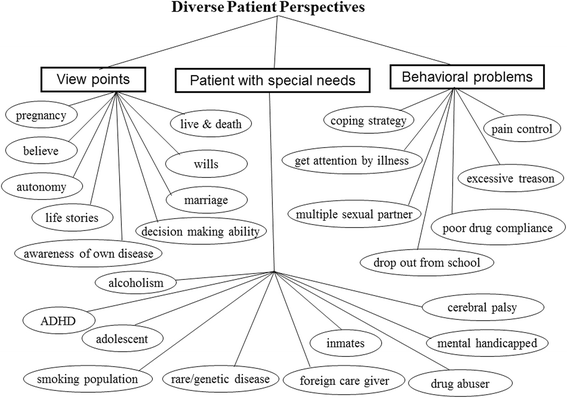
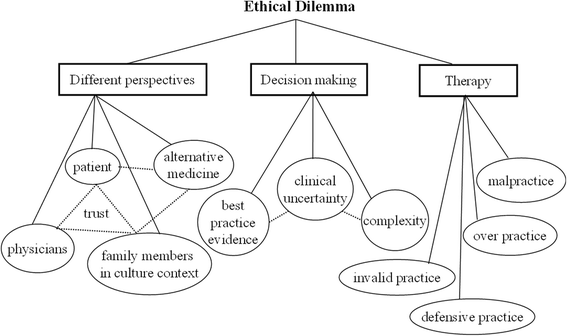
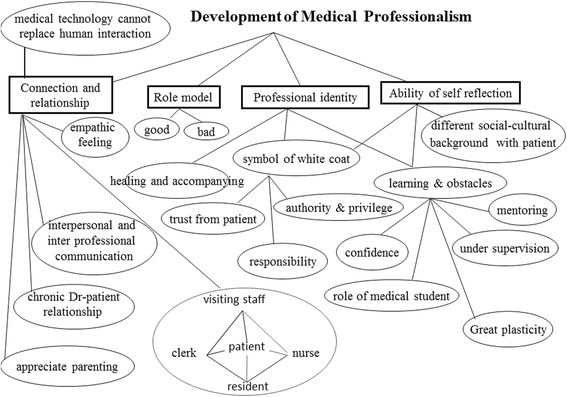
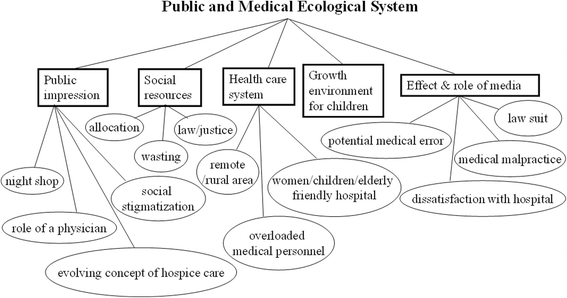
Results: A total of 108 psychosocial issues were coded and categorized as the following six main themes: medical communication, the intricate medical ecological system, role and function of a family, development of medical professionalism, ethical dilemmas, and various patient perspectives from diverse cultural backgrounds. All these themes underlie the complexity of clinical encounters.
Conclusions: Clinical care is an extremely complex interactive ecological network involving human behavior, family, and public health care systems. The discovery of psychosocial problems by medical students as narrators in this study illustrates that medical care should focus not only on illnesses but also patients' psychosocial narratives.
Keywords: Biopsychosocial model; Medical student; Psychosocial issues; Reflective group dialogue; Thematic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Buddhist Tzu Chi General Hospital (IRB NO.: IRB102–20). Since this study was based on a required clinical rotation course, a waiver of informed consent form was granted by the committee (IRB). Nonetheless, as suggested by the IRB, all participants signed a written consent to permit their group dialogues to be recorded and analyzed for the research purpose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that no competing financial, professional or personal interests or activities interest exists that could appear to have influenced the submitted work and arise from the direct applications of our research.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Kliegman R, Stanton B, Geme J St, Scho N. nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Phialdelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016. Chapter 6; Overview and assessment of variability; p. 48–49.
-
- The Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. Biopsychosocial model. 2017. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biopsychosocial_model. Accessed 12 May 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

