Plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote systemic sclerosis with a key role for TLR8
- PMID: 29321259
- PMCID: PMC9865429
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aam8458
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote systemic sclerosis with a key role for TLR8
Abstract
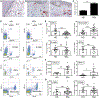
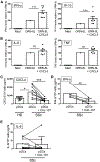
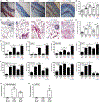
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multisystem life-threatening fibrosing disorder that lacks effective treatment. The link between the inflammation observed in organs such as the skin and profibrotic mechanisms is not well understood. The plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) is a key cell type mediating Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced inflammation in autoimmune disease patients, including lupus and skin diseases with interface dermatitis. However, the role of pDCs in fibrosis is less clear. We show that pDCs infiltrate the skin of SSc patients and are chronically activated, leading to secretion of interferon-α (IFN-α) and CXCL4, which are both hallmarks of the disease. We demonstrate that the secretion of CXCL4 is under the control of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ and is due to the aberrant presence of TLR8 on pDCs of SSc patients, which is not seen in healthy donors or in lupus pDCs, and that CXCL4 primarily acts by potentiating TLR8- but also TLR9-induced IFN production by pDCs. Depleting pDCs prevented disease in a mouse model of scleroderma and could revert fibrosis in mice with established disease. In contrast, the disease was exacerbated in mice transgenic for TLR8 with recruitment of pDCs to the fibrotic skin, whereas TLR7 only partially contributed to the inflammatory response, indicating that TLR8 is the key RNA-sensing TLR involved in the establishment of fibrosis. We conclude that the pDC is an essential cell type involved in the pathogenesis of SSc and its removal using depleting antibodies or attenuating pDC function could be a novel approach to treat SSc patients.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures





References
-
- Ferri C, Valentini G, Cozzi F, Sebastiani M, Michelassi C, La Montagna G, Bullo A, Cazzato M, Tirri E, Storino F, Giuggioli D, Cuomo G, Rosada M, Bombardieri S, Todesco S, Tirri G; Systemic Sclerosis Study Group of the Italian Society of Rheumatology (SIR-GSSSc), Systemic sclerosis: Demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1,012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 81, 139–153 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Mayes MD, Lacey JV Jr., Beebe-Dimmer J, Gillespie BW, Cooper B, Laing TJ, Schottenfeld D, Prevalence, incidence, survival, and disease characteristics of systemic sclerosis in a large US population. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 2246–2255 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa M, Hamaguchi Y, Yanaba K, Bouaziz J-D, Uchida J, Fujimoto M, Matsushita T, Matsushita Y, Horikawa M, Komura K, Takehara K, Sato S, Tedder TF, B-lymphocyte depletion reduces skin fibrosis and autoimmunity in the tight-skin mouse model for systemic sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol 169, 954–966 (2006). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

