Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma: signaling pathways and targeted therapies
- PMID: 29321659
- PMCID: PMC5860944
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-017-0045-7
Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma: signaling pathways and targeted therapies
Abstract
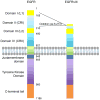
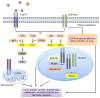
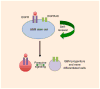
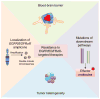
Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its active mutant EGFRvIII occurs frequently in glioblastoma (GBM). While EGFR and EGFRvIII play critical roles in pathogenesis, targeted therapy with EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) or antibodies has only shown limited efficacy in patients. Here we discuss signaling pathways mediated by EGFR/EGFRvIII, current therapeutics, and novel strategies to target EGFR/EGFRvIII-amplified GBM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cloughesy TF, Cavenee WK, Mischel PS. Glioblastoma: from molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annual review of pathology. 2014;9:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta neuropathologica. 2016;131:803–820. - PubMed
-
- Ohgaki H, Kleihues P. The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2013;19:764–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

