Kingiodendron pinnatum, a pharmacologically effective alternative for Saraca asoca in an Ayurvedic preparation, Asokarishta
- PMID: 29322015
- PMCID: PMC5756021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.06.005
Kingiodendron pinnatum, a pharmacologically effective alternative for Saraca asoca in an Ayurvedic preparation, Asokarishta
Abstract
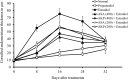
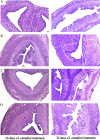
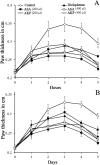
Saraca asoca (Fabaceae) is a prime ingredient in Asokarishta, a well-known Ayurvedic preparation for gynecological ailments. Due to scarcity, adulteration or substitution of related raw drugs is a common practice in its preparation. The bark of Kingiodendron pinnatum (Roxb. ex DC.) Harms, morphologically similar to S. asoca (Asoka) is a widely used substitute. The present study aimed to evaluate the pharmacological effectiveness of K. pinnatum as an alternative for S. asoca in Asokarishta by determining the inhibitory effect of estrogen induced uterus endometrial thickening in immature female rats. Arishta was prepared using S. asoca and with the substitute, K. pinnatum as per Ayurvedic Pharmacopeia. Uterus endometrial thickening was induced by the administration of estradiol (20 μg/kg b. wt, i.p) to 8-day-old rats for 5 alternate days. On day 16, following estradiol administration, the serum estrogen level was found elevated to 156.5 ± 8 pg/ml from the normal value 32.4 ± 5 pg/ml and consequently increased the thickness of uterus endometrium from 16.7 ± 1.4 to 75.2 ± 15.3 μm. Upon oral administration of 400 μl/kg b. wt Asokarishta (ASA) and Arishta made with K. pinnatum (AKP), the thickening was reduced to 42.5 ± 12.7 and 47.1 ± 10.5 μm and the estrogen level diminished to 102.6 ± 10 and 97.3 ± 8 pg/ml, respectively. Arishta also reduced the chronic/acute inflammations in mice and improved the antioxidant status of rats. No toxic symptom was observed in the animals by the treatment of Arishta. The study supports the use of K. pinnatum as an alternative to S. asoca in Asokarishta and gives a scientific validation for Asokarishta in gynecological ailments.
Keywords: Anti-estrogenic; Anti-inflammatory; Asokarishta; Cornification; Metaplasia; Substitutes; Uterus endometrium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Saraca asoca (Asoka) on estradiol-induced keratinizing metaplasia in rat uterus.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;26(5):509-15. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2014-0124. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25915082
-
Activity based evaluation of a traditional Ayurvedic medicinal plant: Saraca asoca (Roxb.) de Wilde flowers as estrogenic agents using ovariectomized rat model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 4;195:324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.038. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27884717
-
DNA barcoding and NMR spectroscopy-based assessment of species adulteration in the raw herbal trade of Saraca asoca (Roxb.) Willd, an important medicinal plant.Int J Legal Med. 2016 Nov;130(6):1457-1470. doi: 10.1007/s00414-016-1436-y. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Int J Legal Med. 2016. PMID: 27627901
-
Anti-inflammatory flavanol glycosides from Saraca asoca bark.Nat Prod Res. 2016;30(4):489-92. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2015.1023728. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Nat Prod Res. 2016. PMID: 25801341
-
Investigating potent cardioprotective compounds as ACE inhibitors in Saraca asoca.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Sep 10;13:101731. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101731. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39309635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mishra L., Singh B.B., Dagenais S. Ayurveda: a historical perspective and principles of the traditional healthcare system in India. Altern Ther Health Med. 2001;7(2):36–42. - PubMed
-
- Patwardhan B. Ayurveda: the designer medicine. Indian Drugs. 2000;37:213–227.
-
- Mukherjee P.K., Harwansh R.K., Bahadur S. Development of Ayurveda – tradition to trend. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016:30782–30786. - PubMed
-
- Dubey N.K., Rajesh K., Pramila T. Global promotion of herbal medicine: India's opportunity. Curr Sci. 2004;86:37–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
