Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo antileishmanial potential of bergenin rich Bergenia ligulata (Wall.) Engl. root extract against visceral leishmaniasis in inbred BALB/c mice through immunomodulation
- PMID: 29322016
- PMCID: PMC5756018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.06.006
Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo antileishmanial potential of bergenin rich Bergenia ligulata (Wall.) Engl. root extract against visceral leishmaniasis in inbred BALB/c mice through immunomodulation
Abstract
Background: Medicinal plants with immunomodulatory properties can provide good alternative therapeutics for curing visceral leishmaniasis. Bergenia ligulata (Wall.) Engl. is an interesting plant with strong antioxidant, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective properties.
Aim: The present study was planned to determine the antileishmanial activity of plant extract by modulating the immune responses of inbred BALB/c mice.
Methodology: Bergenin, the principle active component of B. ligulata, was quantitated in crude extract by performing RP-HPLC. The therapeutic potential was assessed through in vitro antileishmanial activity and in mice model through parasite load, cytokine assays, IgG antibody levels, DTH responses, histopathology and biochemical enzyme assays.
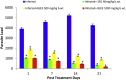
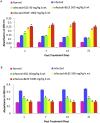
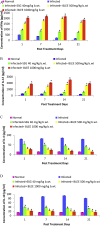
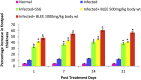
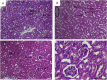
Results: B. ligulata showed the presence of glycosides, saponins, carbohydrates, tannins, flavonoids and bergenin which contributed to the antileishmanial activity of extract with IC50 of 22.70 μg/mL. Furthermore, the higher dose significantly reduced the parasite load by 95.56 %. The reduction was further associated with significant enhancement of IL-12 and IFN-γ levels in comparison to IL-10 and IL-4 cytokines. The switching towards Th1 type of immune response was also confirmed by elevated antibody levels of IgG2a isotype as compared to IgG1 as well as increased DTH responses. The histology of liver and kidney further complimented the non toxic nature of plant extract in addition to its negligible toxicity on HeLa cells.
Conclusions: The current study revealed the significant antileishmanial and immunomodulatory properties of this plant extract against murine visceral leishmaniasis. Further, the bioactive components will be explored to assess their efficacy for the development of safe and cost effective drug.
Keywords: BLEE, Bergenia ligulata ethanolic extract; Biochemical; CMI, Cell mediated immune responses; DCT, Distal convoluted tubules; DMSO, Dimethyl sulphoxide; Extract; HPLC; Histopathological studies; Immunological; PCT, Proximal convoluted tubules; Parasite load; SRBC, Sheep red blood cells; SSG, Sodium stibogluconate; T.S, Transverse section; VL, Visceral leishmaniasis; p.i.d., Post infection days; p.t.d., Post treatment days.
Figures



References
-
- Gellis A., Dume tre A., Lanzada G. Preparation and antiprotozoal evaluation of promising b-carboline alkaloids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2011;66:339–347. - PubMed
-
- Wright C.W. Traditional antimalarials and the development of novel antimalarial drugs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:67–71. - PubMed
-
- WHO Leishmaniasis in high burden countries: an epidemiological update based on data reported in 2014. Wkly Epidemiol. 2016;91:285–296. Rec No. 22. - PubMed
-
- Kaur S., Chauhan K., Sachdeva H. Protection against experimental visceral leishmaniasis by immunostimulation with herbal drugs derived from Withania somnifera and Asparagus racemosus. J Med Microbiol. 2014;63:1328–1338. - PubMed
-
- Dias L.C., de Lima G.M., Pinheiro C.B. Design, structural and spectroscopic elucidation of new nitroaromatic carboxylic acids and semicarbazones for the in vitro screening of anti-leishmanial activity. J Mol Struct. 2015;1079:298–306.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
