Inter-rater agreement of novel high-resolution impedance manometry metrics: Bolus flow time and esophageal impedance integral ratio
- PMID: 29322591
- PMCID: PMC5992008
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13289
Inter-rater agreement of novel high-resolution impedance manometry metrics: Bolus flow time and esophageal impedance integral ratio
Abstract
Background: Novel high-resolution impedance manometry (HRIM) metrics of bolus flow time (BFT) and esophageal impedance integral (EII) ratio have demonstrated clinical utility, though the reliability of their analysis has not been assessed. We aimed to evaluate the inter-rater agreement of the BFT and EII ratio.
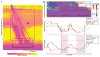
Methods: HRIM studies including five upright, liquid swallows from 40 adult patients were analyzed by two raters using a customized MATLAB program to generate the BFT and EII ratio. Inter-rater agreement was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for median values generated per patient and also for all 200 swallows.
Key results: The ICC (95% confidence interval, CI) for BFT was 0.873 (0.759-0.933) for median values and 0.838 (0.778-0.881) for all swallows. The ICC (95% CI) for EII ratio was 0.983 (0.968-0.991) for median values and 0.905 (0.875-0.928) for all swallows. Median values for both BFT and EII ratio were similar between the two raters (P-values .05).
Conclusions and inferences: The BFT and EII ratio can be reliably calculated as supported by generally excellent inter-rater agreement. Thus, broader utilization of these measures appears feasible and would facilitate further evaluation of their clinical utility.
Keywords: achalasia; dysphagia; high-resolution manometry; impedance; reliability.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Bredenoord AJ, Tutuian R, Smout AJ, et al. Technology review: Esophageal impedance monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(1):187–94. - PubMed
-
- Tutuian R, Castell DO. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry clarifies esophageal function abnormalities: study in 350 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(6):1011–9. - PubMed
-
- Rommel N, Van Oudenhove L, Tack J, et al. Automated impedance manometry analysis as a method to assess esophageal function. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26(5):636–45. - PubMed
-
- Myers JC, Nguyen NQ, Jamieson GG, et al. Susceptibility to dysphagia after fundoplication revealed by novel automated impedance manometry analysis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24(9):812–e393. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen NQ, Holloway RH, Smout AJ, et al. Automated impedance-manometry analysis detects esophageal motor dysfunction in patients who have non-obstructive dysphagia with normal manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(3):238–45. e164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

