Bioresorbable Scaffolds in Coronary Intervention: Unmet Needs and Evolution
- PMID: 29322695
- PMCID: PMC5764868
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0194
Bioresorbable Scaffolds in Coronary Intervention: Unmet Needs and Evolution
Abstract
Bioresorbable scaffolds (BRS) represent a novel paradigm in the 40-year history of interventional cardiology. Restoration of cyclic pulsatility and physiologic vasomotion, adaptive vascular remodeling, plaque regression, and removal of the trigger for late adverse events are expected BRS benefits over current metallic drug-eluting stents. However, first-generation BRS devices have significant manufacturing limitations and rely on optimal implantation technique to avoid experiencing an excess of clinical events. There are currently at least 22 BRS devices in different stages of development, including many trials of device iterations with thinner (<150 μm) struts than first-generation BRS. This article reviews the outcomes of commercially available and potentially upcoming BRS, focusing on the most recent stages of clinical development and future directions for each scaffold type.
Keywords: ABSORB; Angioplasty; Biodegradable stents; Bioresorbable scaffolds; Coronary stents.
Copyright © 2018. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Speaker and consulting fees from Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA.
Figures
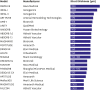

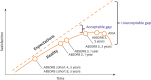
References
-
- Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, et al. Stent thrombosis with drug-eluting stents: is the paradigm shifting? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:1915–1921. - PubMed
-
- Kereiakes DJ, Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Stone GW. Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds for coronary revascularization. Circulation. 2016;134:168–182. - PubMed
-
- Capodanno D, Angiolillo DJ. Antiplatelet therapy after implantation of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds: a review of the published data, practical recommendations, and future directions. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10:425–437. - PubMed
-
- Capodanno D. Bioresorbable scaffolds: clinical outcomes and considerations. Interv Cardiol Clin. 2016;5:357–363. - PubMed
-
- Capodanno D, Gori T, Nef H, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention with everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in routine clinical practice: early and midterm outcomes from the European multicentre GHOST-EU registry. EuroIntervention. 2015;10:1144–1153. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

