Mediator complex component MED13 regulates zygotic genome activation and is required for postimplantation development in the mouse
- PMID: 29325037
- PMCID: PMC6279059
- DOI: 10.1093/biolre/ioy004
Mediator complex component MED13 regulates zygotic genome activation and is required for postimplantation development in the mouse
Abstract
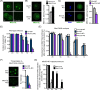
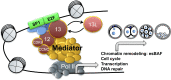
Understanding factors that regulate zygotic genome activation (ZGA) is critical for determining how cells are reprogrammed to become totipotent or pluripotent. There is limited information regarding how this process occurs physiologically in early mammalian embryos. Here, we identify a mediator complex subunit, MED13, as translated during mouse oocyte maturation and transcribed early from the zygotic genome. Knockdown and conditional knockout approaches demonstrate that MED13 is essential for ZGA in the mouse, in part by regulating expression of the embryo-specific chromatin remodeling complex, esBAF. The role of MED13 in ZGA is mediated in part by interactions with E2F transcription factors. In addition to MED13, its paralog, MED13L, is required for successful preimplantation embryo development. MED13L partially compensates for loss of MED13 function in preimplantation knockout embryos, but postimplantation development is not rescued by MED13L. Our data demonstrate an essential role for MED13 in supporting chromatin reprogramming and directed transcription of essential genes during ZGA.
Figures
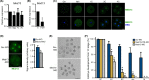
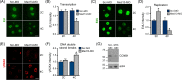
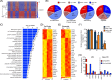

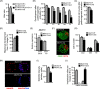
References
-
- Potireddy S, Vassena R, Patel BG, Latham KE. Analysis of polysomal mRNA populations of mouse oocytes and zygotes: dynamic changes in maternal mRNA utilization and function. Dev Biol 2006; 298(1):155–166. - PubMed
-
- Shao GB, Chen JC, Zhang LP, Huang P, Lu HY, Jin J, Gong AH, Sang JR. Dynamic patterns of histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferases and demethylases during mouse preimplantation development. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2014; 50(7):603–613. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre JM, Bocquet S, Terret ME, Namdar M, Ait-Ahmed O, Kearsey S, Verlhac MH, Mechali M. The regulation of competence to replicate in meiosis by Cdc6 is conserved during evolution. Mol Reprod Dev 2004; 69(1):94–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

