A comprehensive Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan shotgun array
- PMID: 29325093
- PMCID: PMC6279168
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwy002
A comprehensive Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan shotgun array
Abstract
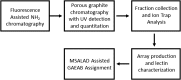
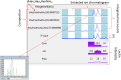
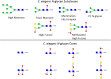
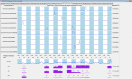
Here we present a Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan shotgun array. This nematode serves as a model organism for many areas of biology including but not limited to tissue development, host-pathogen interactions, innate immunity, and genetics. Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycans contain structural motifs that are also found in other nematodes as well as trematodes and lepidopteran species. Glycan binding toxins that interact with C. elegans glycoconjugates also do so with some agriculturally relevant species, such as Haemonchus contortus, Ascaris suum, Oesophagostomum dentatum and Trichoplusia ni. This situation implies that protein-carbohydrate interactions seen with C. elegans glycans may also occur in other species with related glycan structures. Therefore, this array may be useful to study these relationships in other nematodes as well as trematode and insect species. The array contains 134 distinct glycomers spanning a wide range of C. elegans N-glycans including the subclasses high mannose, pauci mannose, high fucose, mammalian-like complex and phosphorylcholine substituted forms. The glycans presented on the array have been characterized by two-dimensional separation, ion trap mass spectrometry, and lectin affinity. High fucose glycans were well represented and contain many novel core structures found in C. elegans as well as other species. This array should serve as an investigative platform for carbohydrate binding proteins that interact with N-glycans of C. elegans and over a range of organisms that contain glycan motifs conserved with this nematode.
Figures
References
-
- Barrows BD, Haslam SM, Bischof LJ, Morris HR, Dell A, Aroian RV. 2007. Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin in Caenorhabditis elegans from loss of fucose. J Biol Chem. 282:3302–3311. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Spence AM, Schachter H. 2003. Isolation of null alleles of the Caenorhabditis elegans gly-12, gly-13 and gly-14 genes, all of which encode UDP-GlcNAc: Alpha-3-D-mannoside beta1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I activity. Biochimie. 85:391–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

