NHLBI Working Group Recommendations to Reduce Lipoprotein(a)-Mediated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 29325642
- PMCID: PMC5868960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.014
NHLBI Working Group Recommendations to Reduce Lipoprotein(a)-Mediated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
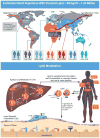
Pathophysiological, epidemiological, and genetic studies provide strong evidence that lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a causal mediator of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD). Specific therapies to address Lp(a)-mediated CVD and CAVD are in clinical development. Due to knowledge gaps, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute organized a working group that identified challenges in fully understanding the role of Lp(a) in CVD/CAVD. These included the lack of research funding, inadequate experimental models, lack of globally standardized Lp(a) assays, and inadequate understanding of the mechanisms underlying current drug therapies on Lp(a) levels. Specific recommendations were provided to facilitate basic, mechanistic, preclinical, and clinical research on Lp(a); foster collaborative research and resource sharing; leverage expertise of different groups and centers with complementary skills; and use existing National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute resources. Concerted efforts to understand Lp(a) pathophysiology, together with diagnostic and therapeutic advances, are required to reduce Lp(a)-mediated risk of CVD and CAVD.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; cardiovascular disease; lipoprotein(a); metabolism; pathophysiology; therapy.
Copyright © 2018 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Tsimikas S. A test in context: Lipoprotein(a): Diagnosis, prognosis, controversies, and emerging therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69:692–711. - PubMed
-
- Langsted A, Nordestgaard BG, Benn M, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Kamstrup PR. PCSK9 R46L Loss-of-Function Mutation Reduces Lipoprotein(a), LDL Cholesterol, and Risk of Aortic Valve Stenosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:3281–7. - PubMed
-
- Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2999–3058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

