CX3CR1+ mononuclear phagocytes control immunity to intestinal fungi
- PMID: 29326275
- PMCID: PMC5805464
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aao1503
CX3CR1+ mononuclear phagocytes control immunity to intestinal fungi
Abstract
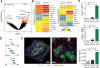
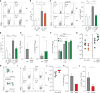
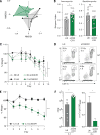
Intestinal fungi are an important component of the microbiota, and recent studies have unveiled their potential in modulating host immune homeostasis and inflammatory disease. Nonetheless, the mechanisms governing immunity to gut fungal communities (mycobiota) remain unknown. We identified CX3CR1+ mononuclear phagocytes (MNPs) as being essential for the initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses to intestinal fungi. CX3CR1+ MNPs express antifungal receptors and activate antifungal responses in a Syk-dependent manner. Genetic ablation of CX3CR1+ MNPs in mice led to changes in gut fungal communities and to severe colitis that was rescued by antifungal treatment. In Crohn's disease patients, a missense mutation in the gene encoding CX3CR1 was identified and found to be associated with impaired antifungal responses. These results unravel a role of CX3CR1+ MNPs in mediating interactions between intestinal mycobiota and host immunity at steady state and during inflammatory disease.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

References
-
- Iliev ID, Funari VA, Taylor KD, Nguyen Q, Reyes CN, Strom SP, Brown J, Becker CA, Fleshner PR, Dubinsky M, Rotter JI, Wang HL, McGovern DP, Brown GD, Underhill DM. Interactions between commensal fungi and the C-type lectin receptor Dectin-1 influence colitis. Science. 2012;336:1314–1317. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

