Spatial effects - site-specific regulation of actin and microtubule organization by septin GTPases
- PMID: 29326311
- PMCID: PMC5818061
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.207555
Spatial effects - site-specific regulation of actin and microtubule organization by septin GTPases
Abstract
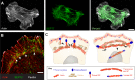
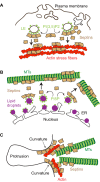
The actin and microtubule cytoskeletons comprise a variety of networks with distinct architectures, dynamics and protein composition. A fundamental question in eukaryotic cell biology is how these networks are spatially and temporally controlled, so they are positioned in the right intracellular places at the right time. While significant progress has been made in understanding the self-assembly of actin and microtubule networks, less is known about how they are patterned and regulated in a site-specific manner. In mammalian systems, septins are a large family of GTP-binding proteins that multimerize into higher-order structures, which associate with distinct subsets of actin filaments and microtubules, as well as membranes of specific curvature and lipid composition. Recent studies have shed more light on how septins interact with actin and microtubules, and raised the possibility that the cytoskeletal topology of septins is determined by their membrane specificity. Importantly, new functions have emerged for septins regarding the generation, maintenance and positioning of cytoskeletal networks with distinct organization and biochemical makeup. This Review presents new and past findings, and discusses septins as a unique regulatory module that instructs the local differentiation and positioning of distinct actin and microtubule networks.
Keywords: Actin; Actin microtubule patterning; Membrane-cytoskeleton crosstalk; Microtubules; Rho signaling; Septins; Spatial organization and regulation.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe author declares no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Masters of asymmetry - lessons and perspectives from 50 years of septins.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Oct 1;31(21):2289-2297. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-11-0648. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32991244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular functions of actin- and microtubule-associated septins.Curr Biol. 2021 May 24;31(10):R651-R666. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.03.064. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34033796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septins mediate a microtubule-actin crosstalk that enables actin growth on microtubules.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 13;119(50):e2202803119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202803119. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36475946 Free PMC article.
-
Septin dynamics and organization in mammalian cells.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024 Dec;91:102442. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102442. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39509956 Review.
-
The state of the septin cytoskeleton from assembly to function.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;68:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.10.007. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33188984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Masters of asymmetry - lessons and perspectives from 50 years of septins.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Oct 1;31(21):2289-2297. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-11-0648. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32991244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SEPT7 Interacts with KIF20A and Regulates the Proliferative State of Neural Progenitor Cells During Cortical Development.Cereb Cortex. 2020 May 14;30(5):3030-3043. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz292. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 31813992 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Cell Cytokinesis: The Rho-Dependent Actomyosin-Anilloseptin Contractile Ring as a Membrane Microdomain Gathering, Compressing, and Sorting Machine.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 7;8:575226. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.575226. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33117802 Free PMC article.
-
Penfluridol targets septin7 to suppress endometrial cancer by septin7-Orai/IP3R-Ca2+-PIK3CA pathway.iScience. 2024 Dec 19;28(1):111640. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111640. eCollection 2025 Jan 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39850355 Free PMC article.
-
Septins as key players in spermatogenesis, fertilisation and pre-implantation embryogenic cytoplasmic dynamics.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 28;22(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01889-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39468561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ageta-Ishihara N., Miyata T., Ohshima C., Watanabe M., Sato Y., Hamamura Y., Higashiyama T., Mazitschek R., Bito H. and Kinoshita M. (2013). Septins promote dendrite and axon development by negatively regulating microtubule stability via HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. Nat. Commun. 4, 2532 10.1038/ncomms3532 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akil A., Peng J., Omrane M., Gondeau C., Desterke C., Marin M., Tronchère H., Taveneau C., Sar S., Briolotti P. et al. (2016). Septin 9 induces lipid droplets growth by a phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate and microtubule-dependent mechanism hijacked by HCV. Nat. Commun. 7, 12203 10.1038/ncomms12203 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

