Thermo-Sensitive TRP Channels: Novel Targets for Treating Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Pain
- PMID: 29326595
- PMCID: PMC5733463
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01040
Thermo-Sensitive TRP Channels: Novel Targets for Treating Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Pain
Abstract
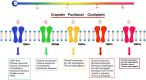
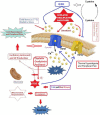
Abnormal Ca2+ channel physiology, expression levels, and hypersensitivity to heat have been implicated in several pain states following treatment with chemotherapeutic agents. As members of the Ca2+ permeable transient receptor potential (TRP), five of the channels (TRPV1-4 and TRPM2) are activated by different heat temperatures, and two of the channels (TRPA1 and TRPM8) are activated by cold temperature. Accumulating evidences indicates that antagonists of TRPA1 and TRPM8 may protect against cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and paclitaxel-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress, inflammation, cold allodynia, and hyperalgesia. TRPV1 was responsible from the cisplatin-induced heat hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in the sensory neurons. TRPA1, TRPM8, and TRPV2 protein expression levels were mostly increased in the dorsal root (DRG) and trigeminal ganglia by these treatments. There is a debate on direct or oxaliplatin-induced oxidative cold stress dependent TRPA1 and TRPV4 activation in the DRG. Involvement of molecular pathways such as cysteine groups, glutathione metabolism, anandamide, cAMP, lipopolysaccharide, proteinase-activated receptor 2, and mitogen-activated protein kinase were also indicated in the oxaliplatin and paclitaxel-induced cold allodynia. In this review, we summarized results of five temperature-regulated TRP channels (TRPA1, TRPM8, TRPV1, TRPV2, and TRPV4) as novel targets for treating chemotherapy-induced peripheral pain.
Keywords: allodynia; chemotherapeutic agents; hyperalgesia; oxidative stress; thermo sensitive TRP channels.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

