Improving Management of Paediatric Buckle Fracture in Orthopaedic Outpatients: A Completed Audit Loop
- PMID: 29326858
- PMCID: PMC5757849
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1829
Improving Management of Paediatric Buckle Fracture in Orthopaedic Outpatients: A Completed Audit Loop
Abstract
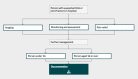
Introduction Paediatric patient bone fractures are the source of a large number of orthopaedic outpatient visits, especially for fracture clinics. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline NG38 provides guidance on assessing and managing non-complex fractures, such as buckle (i.e., torus) fractures in paediatric patients. Objective We retrospectively audited outpatient records of children younger than 12 years presenting with distal radius buckle fractures for May and June 2017. We compared our practice against the NICE guideline standards. We made certain changes in our practice and then repeated the exercise prospectively for two months from July 15 to September 15, 2017. Material and Methods We identified 31 patients who fit our inclusion criteria. After instituting changes based on the NICE guidelines, the number of children included in the prospective data collection was 33 patients. Results For the 31 children treated according to our older protocol, we had 59 outpatient visits, with an average of 1.90 visits for every child. After the NICE-driven changes were made to our management, 33 patients were treated in 39 visits with an average of 1.2 visits per child. Conclusion Introducing NICE guidelines allowed for considerable improvement in the management and treatment of paediatric patient bone fractures. It is important to fully implement the NICE guidelines not only in fracture clinics but also in other departments, such as accident and emergency departments.
Keywords: buckle fracture; nice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Soft cast versus rigid cast for treatment of distal radius buckle fractures in children. Witney-Lagen C, Smith C, Walsh G. Injury. 2013 ;44:508–513. - PubMed
-
- Putting evidence based protocols into practice- a paediatric buckle fracture pathway. Rowlands R, Geelhoed G, Stannage K. Arch Dis Childhood. 2012;97:0–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
