Remote Lifestyle Counseling Influences Cardiovascular Health Outcomes in Youth with Overweight or Obesity and Congenital Heart Disease
- PMID: 29326907
- PMCID: PMC5741592
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2017.00269
Remote Lifestyle Counseling Influences Cardiovascular Health Outcomes in Youth with Overweight or Obesity and Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
Background: Children with overweight/obesity and congenital heart disease (CHD) are at increased cardiovascular risk. A lifestyle intervention may help reduce these risks. We sought to determine the feasibility of a smartphone-based lifestyle intervention to improve cardiovascular health outcomes in children with overweight/obesity and CHD.
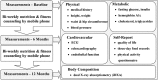
Methods: We examined the effect of bi-weekly nutrition and fitness counseling delivered via smartphone over 12 months. Thirty-four youth, previously diagnosed with CHD and with overweight or obesity, participated in the intervention. They were divided into two groups depending on whether the heart disease required surgical correction (operated, n = 19) or not (non-operated, n = 15). Anthropometry, body composition cardiorespiratory exercise capacity, and cardio-metabolic risk factors were assessed at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months.
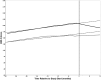
Results: Statistically significant decreases in waist circumference (WC), body mass index z-score, WC z-score, and waist to height ratio z-score were observed at 6 and 12 months in the operated group. A significant linear increase in lean body mass was observed in both groups. The study also had a high retention rate and a low attrition rate.
Conclusion: The observed changes in anthropometry were positive with significant improvement to some cardiovascular and metabolic risk indicators. However, this was only observed in the operated group suggesting that other factors, such as perception of condition and self-efficacy, may influence lifestyle behaviors. The results from this pilot study clearly demonstrate the feasibility to perform a larger controlled study on remote lifestyle intervention in children with congenital heart defects and overweight or obesity.
Keywords: children; congenital heart disease; lifestyle intervention; obesity; remote counseling; smartphone.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

