Fundamentals of siRNA and miRNA therapeutics and a review of targeted nanoparticle delivery systems in breast cancer
- PMID: 29327101
- PMCID: PMC5803180
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-017-0392-1
Fundamentals of siRNA and miRNA therapeutics and a review of targeted nanoparticle delivery systems in breast cancer
Abstract
Gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi) is rapidly evolving as a personalized approach to cancer treatment. The effector molecules-small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs)-can be used to silence or "switch off" specific cancer genes. Currently, the main barrier to implementing siRNA- and miRNA-based therapies in clinical practice is the lack of an effective delivery system that can protect the RNA molecules from nuclease degradation, deliver to them to tumor tissue, and release them into the cytoplasm of the target cancer cells, all without inducing adverse effects. Here, we review the fundamentals of RNAi, cell membrane transport pathways, and factors that affect intracellular delivery. We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the various types of nanoparticle delivery systems, with a focus on those that have been investigated in breast cancer in vivo.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cellular transport; Delivery; MicroRNA; Nanoparticles; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Tamkin Ahmadzada declares that she has no conflict of interest. Glen Reid declares that he has no conflict of interest. David McKenzie declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
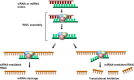

References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Principles of membrane transport. In: Molecular biology of the cell, 4th edn. Garland Science, New York. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26815. Accessed 29 Jul 2017
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

