Genetically‑modified stem cells in treatment of human diseases: Tissue kallikrein (KLK1)‑based targeted therapy (Review)
- PMID: 29328364
- PMCID: PMC5819898
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3361
Genetically‑modified stem cells in treatment of human diseases: Tissue kallikrein (KLK1)‑based targeted therapy (Review)
Abstract
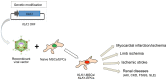
The tissue kallikrein‑kinin system (KKS) is an endogenous multiprotein metabolic cascade which is implicated in the homeostasis of the cardiovascular, renal and central nervous system. Human tissue kallikrein (KLK1) is a serine protease, component of the KKS that has been demonstrated to exert pleiotropic beneficial effects in protection from tissue injury through its anti‑inflammatory, anti‑apoptotic, anti‑fibrotic and anti‑oxidative actions. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) constitute populations of well‑characterized, readily obtainable multipotent cells with special immunomodulatory, migratory and paracrine properties rendering them appealing potential therapeutics in experimental animal models of various diseases. Genetic modification enhances their inherent properties. MSCs or EPCs are competent cellular vehicles for drug and/or gene delivery in the targeted treatment of diseases. KLK1 gene delivery using adenoviral vectors or KLK1 protein infusion into injured tissues of animal models has provided particularly encouraging results in attenuating or reversing myocardial, renal and cerebrovascular ischemic phenotype and tissue damage, thus paving the way for the administration of genetically modified MSCs or EPCs with the human tissue KLK1 gene. Engraftment of KLK1‑modified MSCs and/or KLK1‑modified EPCs resulted in advanced beneficial outcome regarding heart and kidney protection and recovery from ischemic insults. Collectively, findings from pre‑clinical studies raise the possibility that tissue KLK1 may be a novel future therapeutic target in the treatment of a wide range of cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and renal disorders.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

