Western Diet Triggers NLRP3-Dependent Innate Immune Reprogramming
- PMID: 29328911
- PMCID: PMC6324559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.013
Western Diet Triggers NLRP3-Dependent Innate Immune Reprogramming
Abstract
Long-term epigenetic reprogramming of innate immune cells in response to microbes, also termed "trained immunity," causes prolonged altered cellular functionality to protect from secondary infections. Here, we investigated whether sterile triggers of inflammation induce trained immunity and thereby influence innate immune responses. Western diet (WD) feeding of Ldlr-/- mice induced systemic inflammation, which was undetectable in serum soon after mice were shifted back to a chow diet (CD). In contrast, myeloid cell responses toward innate stimuli remained broadly augmented. WD-induced transcriptomic and epigenomic reprogramming of myeloid progenitor cells led to increased proliferation and enhanced innate immune responses. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis in human monocytes trained with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) suggested inflammasome-mediated trained immunity. Consistently, Nlrp3-/-/Ldlr-/- mice lacked WD-induced systemic inflammation, myeloid progenitor proliferation, and reprogramming. Hence, NLRP3 mediates trained immunity following WD and could thereby mediate the potentially deleterious effects of trained immunity in inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: ASC; NLRP3 inflammasome; Western diet feeding; atherosclerosis; epigenetic reprogramming; granulocyte macrophage progenitors; innate immune memory; non-communicable diseases; sterile inflammation; trained immunity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
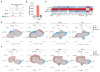
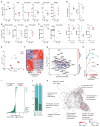


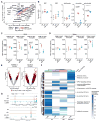
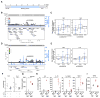
Comment in
-
Immune Training Unlocks Innate Potential.Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.034. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29328917
-
Macrophages Remember Cheeseburgers and Promote Inflammation via NLRP3.Trends Mol Med. 2018 Apr;24(4):335-337. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Trends Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29483038
-
Food for Training-Western Diet and Inflammatory Memory.Cell Metab. 2018 Mar 6;27(3):481-482. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.012. Cell Metab. 2018. PMID: 29514058
-
Training myeloid precursors with fungi, bacteria and chips.Nat Immunol. 2018 Apr;19(4):320-322. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0073-7. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29563630 No abstract available.
-
Trained immunity and cardiovascular disease: is it time for translation to humans?Cardiovasc Res. 2018 May 1;114(6):e41-e42. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy043. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29897493 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bekkering S, Quintin J, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JW, Netea MG, Riksen NP. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces long-term proinflammatory cytokine production and foam cell formation via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:1731–1738. - PubMed
-
- Bekkering S, Arts RJW, Novakovic B, Kourtzelis I, van der Heijden CDCC, Li Y, Popa CD, ter Horst R, van Tuijl J, Netea-Maier RT, et al. Metabolic Induction of Trained Immunity through the Mevalonate Pathway. Cell. 2018:172. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.025. Published online January 11, 2018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boettcher S, Manz MG. Regulation of inflammation- and infection-driven hematopoiesis. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Brasacchio D, Okabe J, Tikellis C, Balcerczyk A, George P, Baker EK, Calkin AC, Brownlee M, Cooper ME, El-Osta A. Hyperglycemia induces a dynamic cooperativity of histone methylase and demethylase enzymes associated with gene-activating epigenetic marks that coexist on the lysine tail. Diabetes. 2009;58:1229–1236. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao X. Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:35–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

