The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer
- PMID: 29328916
- PMCID: PMC5884693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.024
The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer
Erratum in
-
The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer.Cell. 2018 Mar 22;173(1):275. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.024. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29570995 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
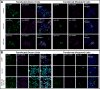
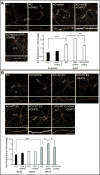
The neuronal gene Arc is essential for long-lasting information storage in the mammalian brain, mediates various forms of synaptic plasticity, and has been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders. However, little is known about Arc's molecular function and evolutionary origins. Here, we show that Arc self-assembles into virus-like capsids that encapsulate RNA. Endogenous Arc protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles that mediate the transfer of Arc mRNA into new target cells, where it can undergo activity-dependent translation. Purified Arc capsids are endocytosed and are able to transfer Arc mRNA into the cytoplasm of neurons. These results show that Arc exhibits similar molecular properties to retroviral Gag proteins. Evolutionary analysis indicates that Arc is derived from a vertebrate lineage of Ty3/gypsy retrotransposons, which are also ancestors to retroviruses. These findings suggest that Gag retroelements have been repurposed during evolution to mediate intercellular communication in the nervous system.
Keywords: Arc; Gag; RNA trafficking; capsid; exosome; extracellular vesicle; retrotransposon; retrovirus; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Cell biology of the neuron: ARC goes viral.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018 Mar;19(3):120-121. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.9. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29386612 No abstract available.
References
-
- Campillos M, Doerks T, Shah PK, Bork P. Computational characterization of multiple Gag-like human proteins. Trends Genet. 2006;22:585–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

