Preparation of Cu₂O-Reduced Graphene Nanocomposite Modified Electrodes towards Ultrasensitive Dopamine Detection
- PMID: 29329206
- PMCID: PMC5795561
- DOI: 10.3390/s18010199
Preparation of Cu₂O-Reduced Graphene Nanocomposite Modified Electrodes towards Ultrasensitive Dopamine Detection
Abstract
Cu₂O-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite (Cu₂O-RGO) was used to modify glassy carbon electrodes (GCE), and applied for the determination of dopamine (DA). The microstructure of Cu₂O-RGO nanocomposite material was characterized by scanning electron microscope. Then the electrochemical reduction condition for preparing Cu₂O-RGO/GCE and experimental conditions for determining DA were further optimized. The electrochemical behaviors of DA on the bare electrode, RGO- and Cu₂O-RGO-modified electrodes were also investigated using cyclic voltammetry in phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS, pH 3.5). The results show that the oxidation peaks of ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA), and uric acid (UA) could be well separated and the peak-to-peak separations are 204 mV (AA-DA) and 144 mV (DA-UA), respectively. Moreover, the linear response ranges for the determination of 1 × 10-8 mol/L~1 × 10-6 mol/L and 1 × 10-6 mol/L~8 × 10-5 mol/L with the detection limit 6.0 × 10-9 mol/L (S/N = 3). The proposed Cu₂O-RGO/GCE was further applied to the determination of DA in dopamine hydrochloride injections with satisfactory results.
Keywords: Cu2O nanoparticles; dopamine detection; electrochemical oxidation; modified electrode; reduced graphene oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


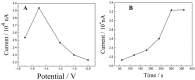
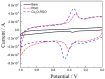



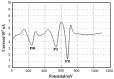

References
-
- Liu A., Honma I., Zhou H. Amperometric biosensor based on tyrosinase-conjugated polysacchride hybrid film: Selective determination of nanomolar neurotransmitters metabolite of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) in biological fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005;21:809–816. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2005.03.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ensafi A.A., Taei M., Khayamian T., Arabzadeh A. Highly selective determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid by differential pulse voltammetry using poly (sulfonazo III) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2010;147:213–221. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.048. - DOI
-
- Li Y., Lin X. Simultaneous electroanalysis of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid by poly (vinyl alcohol) covalently modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2006;115:134–139. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.08.022. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

