RAGE mediates Aβ accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulation of β- and γ-secretase activity
- PMID: 29329433
- PMCID: PMC6075512
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy017
RAGE mediates Aβ accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulation of β- and γ-secretase activity
Abstract
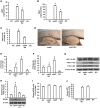
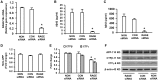
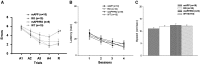
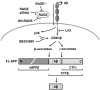
Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products (RAGE) has been implicated in amyloid β-peptide (Aβ)-induced perturbation relevant to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, whether and how RAGE regulates Aβ metabolism remains largely unknown. Aβ formation arises from aberrant cleavage of amyloid pre-cursor protein (APP) by β- and γ-secretase. To investigate whether RAGE modulates β- and γ-secretase activity potentiating Aβ formation, we generated mAPP mice with genetic deletion of RAGE (mAPP/RO). These mice displayed reduced cerebral amyloid pathology, inhibited aberrant APP-Aβ metabolism by reducing β- and γ-secretases activity, and attenuated impairment of learning and memory compared with mAPP mice. Similarly, RAGE signal transduction deficient mAPP mice (mAPP/DN-RAGE) exhibited the reduction in Aβ40 and Aβ42 production and decreased β-and γ-secretase activity compared with mAPP mice. Furthermore, RAGE-deficient mAPP brain revealed suppression of activation of p38 MAP kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β). Finally, RAGE siRNA-mediated gene silencing or DN-RAGE-mediated signaling deficiency in the enriched human APP neuronal cells demonstrated suppression of activation of GSK3β, accompanied with reduction in Aβ levels and decrease in β- and γ-secretases activity. Our findings highlight that RAGE-dependent signaling pathway regulates β- and γ-secretase cleavage of APP to generate Aβ, at least in part through activation of GSK3β and p38 MAP kinase. RAGE is a potential therapeutic target to limit aberrant APP-Aβ metabolism in halting progression of AD.
Figures




References
-
- Selkoe D.J. (1999) Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature, 399, A23–A31. - PubMed
-
- Vassar R., Citron M. (2000) Abeta-generating enzymes: recent advances in beta- and gamma-secretase research. Neuron, 27, 419–422. - PubMed
-
- Nunan J., Shearman M.S., Checler F., Cappai R., Evin G., Beyreuther K., Masters C.L., Small D.H. (2001) The C-terminal fragment of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein precursor is degraded by a proteasome-dependent mechanism distinct from gamma-secretase. Eur. J. Biochem., 268, 5329–5336. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y., Tesco G., Jeong W.J., Lindsley L., Eckman E.A., Eckman C.B., Tanzi R.E., Guenette S.Y. (2003) Generation of the beta-amyloid peptide and the amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragment gamma are potentiated by FE65L1. J. Biol. Chem., 278, 51100–51107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

