Impact of sirtuin-1 expression on H3K56 acetylation and oxidative stress: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with resveratrol supplementation
- PMID: 29330620
- PMCID: PMC5851693
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-017-1097-4
Impact of sirtuin-1 expression on H3K56 acetylation and oxidative stress: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with resveratrol supplementation
Abstract
Aims: Sirtuin-1 (SIRT-1) down-regulation in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been associated with epigenetic markers of oxidative stress. We herein aim to evaluate whether an increase in SIRT-1 expression affects histone 3 acetylation at the 56 lysine residue (H3K56ac) in T2DM patients randomly selected to receive either resveratrol (40 mg or 500 mg) or a placebo for 6 months. The primary outcome is changes in the H3K56ac level by variation in SIRT-1 expression and the secondary outcome is the evidence of association between SIRT-1 level, antioxidant markers (TAS), and metabolic variables.
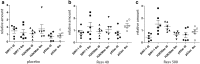
Methods and results: At baseline, peripheral blood mononuclear cell H3K56ac values among the SIRT-1 tertiles did not differ. At trial end, SIRT-1 levels were significantly higher in patients receiving 500 mg resveratrol. At follow-up, patients were divided into tertiles of delta (trial end minus baseline) SIRT-1 value. Significant reductions in H3K56ac and body fat percentage were found in the highest tertile as were increased TAS levels. A multiple logistic regression model showed that the highest delta SIRT-1 tertile was inversely associated with variations in H3K56ac (OR = 0.66; 95% CI 0.44-0.99), TAS (OR = 1.01; 95% CI 1.00-1.02), and body fat percentage (OR = 0.75; 95% CI 0.58-0.96).
Conclusions: We provide new knowledge on H3K56ac and SIRT-1 association in T2DM. These data suggest that boosting SIRT-1 expression/activation may impact redox homeostasis in these patients. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT02244879.
Keywords: Epigenetics; PBMC; Resveratrol; Sirtuin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

