The role of T2*-weighted gradient echo in the diagnosis of tumefactive intrahepatic extramedullary hematopoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome and diffuse hepatic iron overload: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 29332607
- PMCID: PMC5767976
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1531-9
The role of T2*-weighted gradient echo in the diagnosis of tumefactive intrahepatic extramedullary hematopoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome and diffuse hepatic iron overload: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Extramedullary hematopoiesis is the proliferation of hematopoietic cells outside bone marrow secondary to marrow hematopoiesis failure. Extramedullary hematopoiesis rarely presents as a mass-forming hepatic lesion; in this case, imaging-based differentiation from primary and metastatic hepatic neoplasms is difficult, often leading to biopsy for definitive diagnosis. We report a case of tumefactive hepatic extramedullary hematopoiesis in the setting of myelodysplastic syndrome with concurrent hepatic iron overload, and the role of T2*-weighted gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating extramedullary hematopoiesis from primary and metastatic hepatic lesions. To the best of our knowledge, T2*-weighted gradient-echo evaluation of extramedullary hematopoiesis in the setting of diffuse hepatic hemochromatosis has not been previously described.
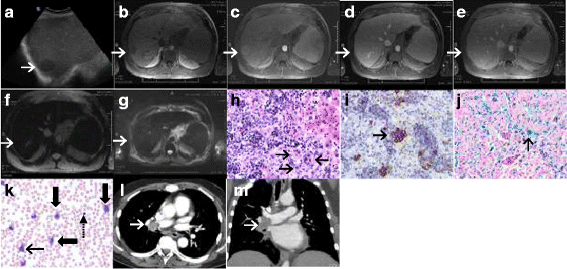
Case presentation: A 52-year-old white man with myelodysplastic syndrome and marrow fibrosis was found to have a 4 cm hepatic lesion on ultrasound during workup for bone marrow transplantation. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed diffuse hepatic iron overload and non-visualization of the lesion on T2* gradient-echo sequence suggesting the presence of iron deposition within the lesion similar to that in background hepatic parenchyma. Subsequent ultrasound-guided biopsy of the lesion revealed extramedullary hematopoiesis. Six months later, while still being evaluated for bone marrow transplant, our patient was found to have poor pulmonary function tests. Follow-up computed tomography angiogram showed a mass within his right main pulmonary artery. Bronchoscopic biopsy of this mass once again revealed extramedullary hematopoiesis. He received radiation therapy to his chest. However, 2 weeks later, he developed mediastinal hematoma and died shortly afterward, secondary to respiratory arrest.
Conclusions: Mass-forming extramedullary hematopoiesis is rare; however, our report emphasizes that it needs to be considered in the initial differential diagnosis of hepatic lesions arising in the setting of bone marrow disorders. We also show that in the setting of diffuse hepatic iron overload, tumefactive extramedullary hematopoiesis appeared isointense to background liver on T2* gradient-echo sequence, while adenoma, hepatoma, and hepatic metastasis appear hyperintense. Thus, T2*-weighted gradient-echo sequence may have a potential role in the imaging diagnosis of mass-forming hepatic extramedullary hematopoiesis arising in the setting of diffuse iron overload.
Keywords: Hepatic extramedullary hematopoiesis; Iron; MRI; Myelodysplastic syndrome; T2*.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s next of kin for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Aydinok Y, Porter JB, Piga A, Elalfy M, El-Beshlawy A, Kilinç Y, et al. Prevalence and distribution of iron overload in patients with transfusion-dependent anemias differs across geographic regions: Results from the CORDELIA study. Eur J Haematol. 2015;95(3):244–53. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12487. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

