The effect of thiamine and its metabolites on peripheral neuropathic pain induced by cisplatin in rats
- PMID: 29332858
- PMCID: PMC5955757
- DOI: 10.1538/expanim.17-0090
The effect of thiamine and its metabolites on peripheral neuropathic pain induced by cisplatin in rats
Abstract
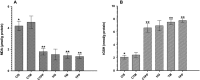
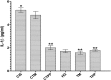
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is the active metabolite of thiamine. This study aimed to investigate the effects of thiamine and TPP on cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain (PNP). Male albino Wistar type Rattus norvegicus were divided into six groups (n=6) that received 2 mg/kg cisplatin (CIS), 25 mg/kg thiamine (TM), 2 mg/kg cisplatin+25 mg/kg thiamine (CTM), 25 mg/kg TPP (TPP), 2 mg/kg cisplatin+25 mg/kg TPP (CTPP), or distilled water (healthy group; HG) for 8 days intraperitoneally. Analgesic effect was measured with a Basile Algesimeter. IL-1β, malondialdehyde (MDA), total glutathione (tGSH), thiamine, and TPP were determined in blood samples. Histopathological examinations were performed on removed sciatic nerves. The percent analgesic effects of the CTM and CTPP groups were calculated to be 21.3% and 82.9%, respectively. Increased production of IL-1β and MDA by cisplatin was inhibited by TPP, while it was not inhibited by thiamine. Conversion of thiamine to TPP significantly decreased in the CIS group. Histopathological and biochemical investigations demonstrated that hyperalgesia and sciatic nerve damage developed in the CIS and CTM groups with low TPP levels. These results indicate that cisplatin inhibits the formation of TPP from thiamine, leading to severe PNP. This finding suggests that TPP may be more beneficial than thiamine for the treatment of cisplatin-induced PNP.
Keywords: cisplatin; pain; peripheral neuropathy; rat; thiamine..
Figures





References
-
- Aksoy M., Ahiskalioglu A., Ince I., Celik M., Dostbil A., Kuyrukluyildiz U., Altuner D., Kurt N., Suleyman H.2015. The relation between the effect of a subhypnotic dose of thiopental on claw pain threshold in rats and adrenalin, noradrenalin and dopamine levels. Exp. Anim. 64: 391–396. doi: 10.1538/expanim.15-0028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

