Clinical Utility and Measurement of Procalcitonin
- PMID: 29332972
- PMCID: PMC5759088
Clinical Utility and Measurement of Procalcitonin
Abstract
Procalcitonin (PCT), regarded as a biomarker specific for bacterial infections, is used in a variety of clinical settings including primary care, emergency department and intensive care. PCT measurement aids in the diagnosis of sepsis and to guide and monitor antibiotic therapy. This article gives a brief overview of PCT and its use in guiding antibiotic therapy in various clinical settings, as well as its limitations. PCT performance in comparison with other biomarkers of infection in particular CRP is also reviewed. Owing to its greater availability, CRP has been widely used as a biomarker of infection and sepsis. PCT is often reported to be more superior to CRP, being more specific for sepsis and bacterial infection. PCT starts to rise earlier and returns to normal concentration more rapidly than CRP, allowing for an earlier diagnosis and better monitoring of disease progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: None declared.
Figures
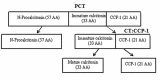
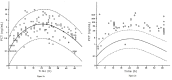
References
-
- Stolz D, Christ-Crain M, Bingisser R, Leuppi J, Miedinger D, Müller C, et al. Antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD: a randomized, controlled trial comparing procalcitonin-guidance with standard therapy. Chest. 2007;131:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Briel M, Schuetz P, Mueller B, Young J, Schild U, Nusbaumer C, et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic use vs a standard approach for acute respiratory tract infections in primary care. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:2000–7. discussion 2007–8. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1589–96. - PubMed
-
- Sykes A, Johnston SL. Etiology of asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:685–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
