Development and validation of High-performance Thin-layer Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Determination of Polyphenolic Compounds in Medicinal Plants
- PMID: 29333046
- PMCID: PMC5757330
- DOI: 10.4103/pr.pr_122_16
Development and validation of High-performance Thin-layer Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Determination of Polyphenolic Compounds in Medicinal Plants
Abstract
Context: Quantitative standardization of plant-based products is challenging albeit essential to maintain their quality.
Aims: This study aims to develop and validate high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) method for the simultaneous determination of rutin (Ru), quercetin (Qu), and gallic acid (Ga) from Psidium guajava Linn. (PG) and Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa. (AM) and correlate with antioxidant activity.
Materials and methods: The stock solution (1 mg/mL) of standard Ru, Qu, and Ga in methanol: Water (1:1) was serially diluted and spotted (5 μL) on slica gel 60 F254 thin-layer chromatography plates. Toluene: Ethyl acetate: Formic acid: Methanol (3:4:0.8:0.7, v/v/v) was selected as mobile phase for analysis at 254 nm. Hydroalcoholic (1:1) extracts of leaves of PG and AM were fractionated and similarly analyzed. Antioxidant activity was also determined using 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay.
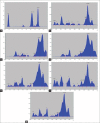
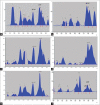
Results: The developed method was robust and resolved Ru, Qu, and Ga at Rf 0.08 ± 0.02, 0.76 ± 0.01, and 0.63 ± 0.02, respectively. The intra-day, interday precision, and interanalyst were <2% relative standard deviation. The limit of detection and limit of quantification for Ru, Qu, and Ga were 4.51, 4.2, 5.27, and 13.67, 12.73, 15.98 ng/spot, respectively. Antioxidant activity (Log 50% inhibition) of PG and AM was 4.947 ± 0.322 and 6.498 ± 0.295, respectively.
Conclusion: The developed HPTLC method was rapid, accurate, precise, reproducible, and specific for the simultaneous estimation of Ru, Qu, and Ga.
Summary: HPTLC method for simultaneous determination and quantification of Rutin, Quercetin and Gallic acid, is reported for quality control of herbal drugs.Abbreviations Used: A: Aqueous fraction; AM: Aegle marmelos L. Correa; B: Butanol fraction; C: Chloroform fraction; EA: Ethyl acetate fraction; Ga: Gallic acid; H: Hexane fraction; HA: Hydroalcoholic extract; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; PG: Psidium guajava; Qu: Quercetin; Ru: Rutin.
Keywords: Aegle marmelos; Psidium guajava; gallic acid; high-performance thin-layer chromatography; quercetin; rutin.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Scalbert A, Williamson G. Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J Nutr. 2000;130:2073S–85S. - PubMed
-
- Kelly GS. Quercetin. Monograph. Altern Med Rev. 2011;16:172–94. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Ali A, Ali J, Sahni JK, Baboota S. Rutin: Therapeutic potential and recent advances in drug delivery. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013;22:1063–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
