Purification, Characterization, and Mode of Action of Pentocin JL-1, a Novel Bacteriocin Isolated from Lactobacillus pentosus, against Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 29333451
- PMCID: PMC5733122
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7657190
Purification, Characterization, and Mode of Action of Pentocin JL-1, a Novel Bacteriocin Isolated from Lactobacillus pentosus, against Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
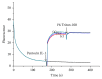
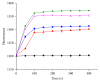
Staphylococcus aureus and its drug-resistant strains, which threaten public health and food safety, are in need of effective control by biopreservatives. A novel bacteriocin, pentocin JL-1, produced by Lactobacillus pentosus that was isolated from the intestinal tract of Chiloscyllium punctatum, was purified by a four-step chromatographic process. Mass spectrometry based on MALDI-TOF indicated that pentocin JL-1 has a molecular mass of 2987.23 Da. Only six of the twenty-five amino acids could be identified by Edman degradation. This bacteriocin is thermostable and tolerates a pH range of 5-7. Also, it is sensitive to proteinase K, trypsin, pepsin, and alkaline protease. This bacteriocin has a broad inhibitory spectrum against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains and in particular is effective against multidrug-resistant S. aureus. Additionally, we showed that the cell membrane is the target of pentocin JL-1 against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), causing a loss of proton motive force. Furthermore, pentocin JL-1 has a drastic impact on the structure and integrity of MRSA cells. These results suggest that pentocin JL-1 has potential as a biopreservative in the food industry.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

