Characteristics of Smoothing Filters to Achieve the Guideline Recommended Positron Emission Tomography Image without Harmonization
- PMID: 29333463
- PMCID: PMC5765329
- DOI: 10.22038/aojnmb.2017.26684.1186
Characteristics of Smoothing Filters to Achieve the Guideline Recommended Positron Emission Tomography Image without Harmonization
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study is to examine the effect of different smoothing filters on the image quality and SUVmax to achieve the guideline recommended positron emission tomography (PET) image without harmonization.
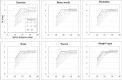
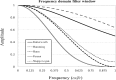
Methods: We used a Biograph mCT PET scanner. A National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) body phantom was filled with 18F solution with a background activity of 2.65 kBq/mL and a sphere-to-background ratio of 4. PET images obtained with the Biograph mCT PET scanner were reconstructed using the ordered subsets-expectation maximization (OSEM) algorithm with time-of-flight (TOF) models (iteration, 2; subset, 21); smoothing filters including the Gaussian, Butterworth, Hamming, Hann, Parzen, and Shepp-Logan filters with various full width at half maximum (FWHM) values (1-15 mm) were applied. The image quality was physically assessed according to the percent contrast (QH,10), background variability (N10), standardized uptake value (SUV), and recovery coefficient (RC). The results were compared with the guideline recommended range proposed by the Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine and the Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine Technology. The PET digital phantom was developed from the digital reference object (DRO) of the NEMA IEC body phantom smoothed using a Gaussian filter with a 10-mm FWHM and defined as the reference image. The difference in the SUV between the PET image and the reference image was evaluated according to the root mean squared error (RMSE).
Results: The FWHMs of the Gaussian, Butterworth, Hamming, Hann, Parzen, and Shepp-Logan filters that satisfied the image quality of the FDG-PET/CT standardization guideline criteria were 8-12 mm, 9-11 mm, 9-13 mm, 10-13 mm, 9-11 mm, and 12-15 mm, respectively. The FWHMs of the Gaussian, Butterworth, Hamming, Hann, Parzen, and Shepp-Logan filters that provided the smallest RMSE between the PET images and the 3D digital phantom were 7 mm, 8 mm, 8 mm, 8 mm, 7 mm, and 11 mm, respectively.
Conclusion: The suitable FWHM for image quality or SUVmax depends on the type of smoothing filter that is applied.
Keywords: FDG PET; SUV; Smoothing filter.
Figures




References
-
- Fletcher JW, Djulbegovic B, Soares HP, Siegel BA, Lowe VJ, Lyman GH, et al. Recommendations on the use of 18F-FDG PET in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(3):480–508. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Haim S, Ell P. 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT in the evaluation of cancer treatment response. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(1):88–99. - PubMed
-
- Gupta T, Master Z, Kannan S, Agarwal JP, Ghsoh-Laskar S, Rangarajan V, et al. Diagnostic performance of post-treatment FDG PET or FDG PET/CT imaging in head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38(11):2083–95. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson T, Hicks RJ, Peterson A, Port RE. 18F-FDG PET as a surrogate biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib: newly identified lesions are more informative than standardized uptake value. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(4):530–7. - PubMed
-
- Hicks RJ. Role of 18F-FDG PET in assessment of response in non-small cell lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(Suppl 1):31S–42S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
