Activation of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Reverses Cognitive and Respiratory Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome
- PMID: 29333487
- PMCID: PMC5762598
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0277-17.2017
Activation of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Reverses Cognitive and Respiratory Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome
Abstract
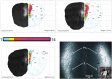
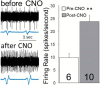
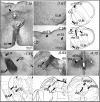
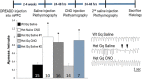
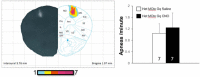
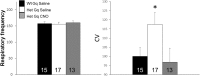
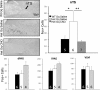
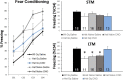
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a severe neurodevelopmental disorder caused by loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2; Amir et al., 1999), a transcriptional regulatory protein (Klose et al., 2005). Mouse models of RTT (Mecp2 mutants) exhibit excitatory hypoconnectivity in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC; Sceniak et al., 2015), a region critical for functions that are abnormal in RTT patients, ranging from learning and memory to regulation of visceral homeostasis (Riga et al., 2014). The present study was designed to test the hypothesis that increasing the activity of mPFC pyramidal neurons in heterozygous female Mecp2 mutants (Hets) would ameliorate RTT-like symptoms, including deficits in respiratory control and long-term retrieval of auditory conditioned fear. Selective activation of mPFC pyramidal neurons in adult animals was achieved by bilateral infection with an AAV8 vector expressing excitatory hm3D(Gq) DREADD (Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs) (Armbruster et al., 2007) under the control of the CamKIIa promoter. DREADD activation in Mecp2 Hets completely restored long-term retrieval of auditory conditioned fear, eliminated respiratory apneas, and reduced respiratory frequency variability to wild-type (Wt) levels. Reversal of respiratory symptoms following mPFC activation was associated with normalization of Fos protein levels, a marker of neuronal activity, in a subset of brainstem respiratory neurons. Thus, despite reduced levels of MeCP2 and severe neurological deficits, mPFC circuits in Het mice are sufficiently intact to generate normal behavioral output when pyramidal cell activity is increased. These findings highlight the contribution of mPFC hypofunction to the pathophysiology of RTT and raise the possibility that selective activation of cortical regions such as the mPFC could provide therapeutic benefit to RTT patients.
Keywords: DREADD; Mecp2; autism spectrum disorder; hypofrontality; mPFC; memory.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander GM, Rogan SC, Abbas AI, Armbruster BN, Pei Y, Allen JA, Nonneman RJ, Hartmann J, Moy SS, Nicolelis MA, McNamara JO, Roth BL (2009) Remote control of neuronal activity in transgenic mice expressing evolved G protein-coupled receptors. Neuron 63:27–39. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov VG, Ivanova TG, Alexandrova NP (2007) Prefrontal control of respiration. J Physiol Pharmacol 58 [Suppl 5]:17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
