Surrogate scale for evaluating respiratory function based on complete blood count parameters
- PMID: 29333619
- PMCID: PMC6817169
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22385
Surrogate scale for evaluating respiratory function based on complete blood count parameters
Abstract
Background: In this study, we aimed to identify a simple method for evaluating respiratory function using complete blood count parameters.
Methods: The complete blood count parameters, including red blood cell (RBC) count, hemoglobin (Hb) level, lymphocyte (Lym) and platelet (Plt) count, and partial pressure of oxygen (PO2 ) level, were measured using automated analyzers in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), aged subjects, and young subjects (control group). The red cell index (RCI) was calculated using the following equation: (RBC × Hb)/(Lym × Plt); in theory, the RCI is inversely proportional to the respiratory function.
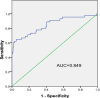
Results: We observed a significant relationship between the RCI and PCO2 values, and between the RCI and FEV1/FVC values (P < .05). The RCI in the COPD, and aged subject groups were all significantly higher than that in the control group (P < .05). The cutoff value for normal respiratory function was 2.3. The positive rates for an abnormal increase in RCI were also considerably higher in each observation group than in the control group (P < .05).
Conclusion: The RCI can be considered as a simple and effective tool for evaluating respiratory function.
Keywords: COPD; blood count; computer-assisted diagnosis; respiratory function.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Elojeimy S, Cruite I, Bowen S, Zeng J, Vesselle H. Overview of the novel and improved pulmonary ventilation‐perfusion imaging applications in the era of SPECT/CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207:1307‐1315. - PubMed
-
- Hage JJ, Brinkman RJ. Andreas Vesalius’ understanding of pulmonary ventilation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2016;231:37‐44. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lee JS, et al. Relative versus absolute change in forced vital capacity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 2012;67:407‐411. - PubMed
-
- Bateman SW. Making sense of blood gas results. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2008;38:543‐557. - PubMed
-
- Crawford A. An audit of the patient's experience of arterial blood gas testing. Br J Nurs. 2004;13:529‐532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical