The innate immune system in chronic cardiomyopathy: a European Society of Cardiology (ESC) scientific statement from the Working Group on Myocardial Function of the ESC
- PMID: 29333691
- PMCID: PMC5993315
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1138
The innate immune system in chronic cardiomyopathy: a European Society of Cardiology (ESC) scientific statement from the Working Group on Myocardial Function of the ESC
Abstract
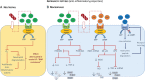
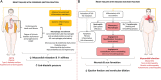
Activation of the immune system in heart failure (HF) has been recognized for over 20 years. Initially, experimental studies demonstrated a maladaptive role of the immune system. However, several phase III trials failed to show beneficial effects in HF with therapies directed against an immune activation. Preclinical studies today describe positive and negative effects of immune activation in HF. These different effects depend on timing and aetiology of HF. Therefore, herein we give a detailed review on immune mechanisms and their importance for the development of HF with a special focus on commonalities and differences between different forms of cardiomyopathies. The role of the immune system in ischaemic, hypertensive, diabetic, toxic, viral, genetic, peripartum, and autoimmune cardiomyopathy is discussed in depth. Overall, initial damage to the heart leads to disease specific activation of the immune system whereas in the chronic phase of HF overlapping mechanisms occur in different aetiologies.
Keywords: Autoimmune cardiomyopathy; Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Genetic cardiomyopathy; Hypertensive cardiomyopathy; Immune system; Ischaemic cardiomyopathy; Macrophage; Peripartum cardiomyopathy; T-cell; Toxic cardiomyopathy; Viral cardiomyopathy.
© 2018 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Levine B, Kalman J, Mayer L, Fillit HM, Packer M. Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 1990;323:236–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

