Targeting BRD4 proteins suppresses the growth of NSCLC through downregulation of eIF4E expression
- PMID: 29333921
- PMCID: PMC5915014
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1423923
Targeting BRD4 proteins suppresses the growth of NSCLC through downregulation of eIF4E expression
Abstract
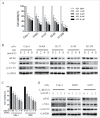
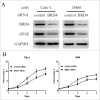
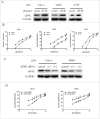
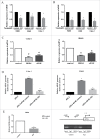
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) proteins act as epigenome readers for gene transcriptional regulation. Among BET family members, BRD4 was well studied, but for its mechanism in non-small cell lung carcinoma has not been elucidated. eIF4E regulates gene translation and has been proved to play an important role in the progression of lung cancer. In this study, we first confirmed that BET inhibitors JQ1 and I-BET151 suppressed the growth of NSCLCs, in parallel with downregulated eIF4E expression. Then we found that knockdown of BRD4 expression using siRNAs inhibited the growth of NSCLCs as well as decreased eIF4E protein levels. Moreover, overexpression of eIF4E partially abrogated the growth inhibitory effect of JQ1, while knockdown of eIF4E enhanced the inhibitory effect of JQ1. Furthermore, JQ1 treatment or knockdown of BRD4 expression decreased eIF4E mRNA levels and inhibited its promoter activity by luciferase reporter assay. JQ1 treatment significantly decreased the binding of eIF4E promoter with BRD4. Finally, JQ1 inhibited the growth of H460 tumors in parallel with downregulated eIF4E mRNA and protein levels in a xenograft mouse model. These findings suggest that inhibition of BET by JQ1, I-BET151, or BRD4 silencing suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung carcinoma through decreasing eIF4E transcription and subsequent mRNA and protein expression. Considering that BET regulates gene transcription epigenetically, our findings not only reveal a new mechanism of BET-regulated eIF4E in lung cancer, but also indicate a novel strategy by co-targeting eIF4E for enhancing BET-targeted cancer therapy.
Keywords: BRD4; eIF4E; epigenetics; molecular targeted therapy; non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of BET bromodomain-dependent XIAP and FLIP expression sensitizes KRAS-mutated NSCLC to pro-apoptotic agents.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Sep 8;7(9):e2365. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.271. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27607580 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting BET proteins inhibited the growth of non-small cell lung carcinoma through downregulation of Met expression.Cell Biol Int. 2023 Mar;47(3):622-633. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11962. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Cell Biol Int. 2023. PMID: 36448366
-
Bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibition synergizes with WEE1-inhibitor AZD1775 effect by impairing nonhomologous end joining and enhancing DNA damage in nonsmall cell lung cancer.Int J Cancer. 2020 Feb 15;146(4):1114-1124. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32515. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31199520
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors--a novel epigenetic approach in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1583-5. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962297. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25535892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JQ1: a novel potential therapeutic target.Pharmazie. 2018 Sep 1;73(9):491-493. doi: 10.1691/ph.2018.8480. Pharmazie. 2018. PMID: 30223929 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting sphingosine kinase 1/2 by a novel dual inhibitor SKI-349 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jul 12;13(7):602. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05049-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35831279 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-612 suppresses the malignant development of non-small-cell lung cancer by directly targeting bromodomain-containing protein 4.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 28;12:4167-4179. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S204004. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Sep 09;14:4745-4746. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S337587. PMID: 31213835 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Biological functions and research progress of eIF4E.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 3;13:1076855. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1076855. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37601696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_0000376 downregulation inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the miR-488-3p/BRD4 axis and the PI3K/PKB signaling pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2021 Dec;36(12):1309-1324. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-390. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Histol Histopathol. 2021. PMID: 34730838
-
Induction of MNK Kinase-dependent eIF4E Phosphorylation by Inhibitors Targeting BET Proteins Limits Efficacy of BET Inhibitors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Feb;18(2):235-244. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0768. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30446586 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
