Whole Body MRI and oncology: recent major advances
- PMID: 29334236
- PMCID: PMC6350480
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170664
Whole Body MRI and oncology: recent major advances
Abstract
MRI is a very attractive approach for tumour detection and oncological staging with its absence of ionizing radiation, high soft tissue contrast and spatial resolution. Less than 10 years ago the use of Whole Body MRI (WB-MRI) protocols was uncommon due to many limitations, such as the forbidding acquisition times and limited availability. This decade has marked substantial progress in WB-MRI protocols. This very promising technique is rapidly arising from the research world and is becoming a commonly used examination for tumour detection due to recent technological developments and validation of WB-MRI by multiple studies and consensus papers. As a result, WB-MRI is progressively proposed by radiologists as an efficient examination for an expanding range of indications. As the spectrum of its uses becomes wider, radiologists will soon be confronted with the challenges of this technique and be urged to be trained in order to accurately read and report these examinations. The aim of this review is to summarize the validated indications of WB-MRI and present an overview of its most recent advances. This paper will briefly discuss how this examination is performed and which are the recommended sequences along with the future perspectives in the field.
Figures

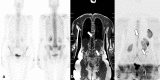
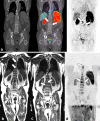
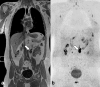
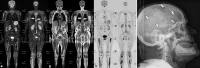
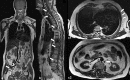
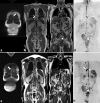
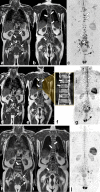
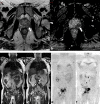
References
-
- Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 2004; 22: 275–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

