Italian guidelines on the assessment and management of pediatric head injury in the emergency department
- PMID: 29334996
- PMCID: PMC5769508
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-017-0442-0
Italian guidelines on the assessment and management of pediatric head injury in the emergency department
Abstract
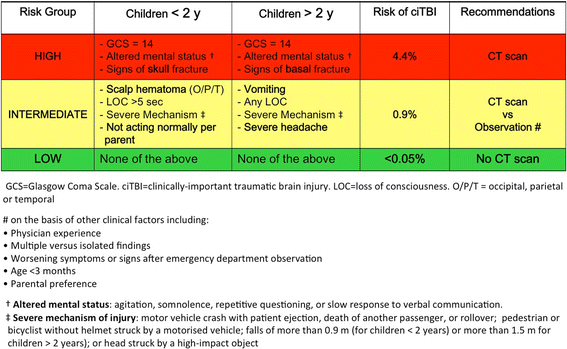
Objective: We aim to formulate evidence-based recommendations to assist physicians decision-making in the assessment and management of children younger than 16 years presenting to the emergency department (ED) following a blunt head trauma with no suspicion of non-accidental injury.
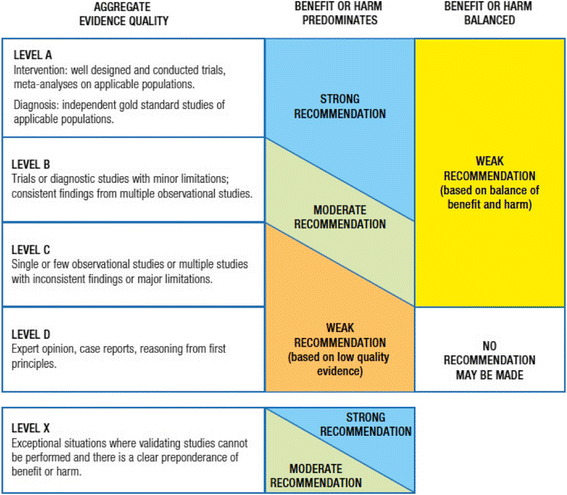
Methods: These guidelines were commissioned by the Italian Society of Pediatric Emergency Medicine and include a systematic review and analysis of the literature published since 2005. Physicians with expertise and experience in the fields of pediatrics, pediatric emergency medicine, pediatric intensive care, neurosurgery and neuroradiology, as well as an experienced pediatric nurse and a parent representative were the components of the guidelines working group. Areas of direct interest included 1) initial assessment and stabilization in the ED, 2) diagnosis of clinically important traumatic brain injury in the ED, 3) management and disposition in the ED. The guidelines do not provide specific guidance on the identification and management of possible associated cervical spine injuries. Other exclusions are noted in the full text.
Conclusions: Recommendations to guide physicians practice when assessing children presenting to the ED following blunt head trauma are reported in both summary and extensive format in the guideline document.
Keywords: Children; Emergency department; Evidence-based; Guideline; Traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors have no financial interests to disclose with respect to the development of the present guidelines. The Italian Society of Pediatric Emergency Medicine and the Italian Society of Pediatrics have neither solicited nor accepted any commercial involvement in the development of the content of this publication.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Peden M, Oyegbite K, Ozanne-smith J, Hyder AA, Branche C, Rahman A, et al., editors. World report on child injury prevention. Geneva: WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee; 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical