[Expression of plasma miRNA-497 in children with sepsis-induced myocardial injury and its clinical significance]
- PMID: 29335079
- PMCID: PMC7390325
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2018.01.007
[Expression of plasma miRNA-497 in children with sepsis-induced myocardial injury and its clinical significance]
Abstract
Objective: To study the expression of plasma miRNA-497 in children with sepsis-induced myocardial injury and its clinical significance.
Methods: A total of 148 children with sepsis were enrolled. According to the presence or absence of myocardial injury, these children were divided into myocardial injury group (n=58) and non-myocardial injury group (n=90). The two groups were compared in terms of the changes in plasma levels of miRNA-497, cardiac troponin I (cTnI), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), procalcitonin (PCT), and C-reactive protein (CRP) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to evaluate the value of plasma miRNA-497, cTnI, and CK-MB in the diagnosis of myocardial injury. A Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine the correlation of miRNA-497 with cTnI, CK-MB, NT-proBNP, PCT, CRP, and LVEF.
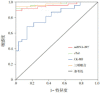
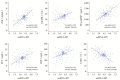
Results: Compared with the non-myocardial injury group, the myocardial injury group had significantly higher plasma levels of miRNA-497, cTnI, CK-MB, NT-proBNP, PCT, and CRP (P<0.05). Plasma miRNA-497, cTnI, and CK-MB when measured alone or in combination had an area under the ROC curve of 0.918, 0.931, 0.775, and 0.940 respectively. At the optimal cut-off value of 2.05, miRNA-497 had a sensitivity of 90.4% and a specificity of 91.2%. The correlation analysis showed that there was a good correlation between plasma miRNA-497 and cTnI in children with myocardial injury (r=0.728, P<0.01).
Conclusions: Plasma miRNA-497 has a similar value as cTnI in the diagnosis of sepsis-induced myocardial injury in children and may be used as a potential marker for early diagnosis of myocardial injury.
目的: 探讨血浆miRNA-497在小儿脓毒症心肌损伤中的表达及其临床意义。
方法: 纳入148例脓毒症患儿,依据其是否发生心肌损伤分为心肌损伤组(58例)和非心肌损伤组(90例),比较两组血浆miRNA-497、心肌肌钙蛋白I (cTnI)、肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)、N末端B型钠尿肽前体(NT-proBNP)、降钙素原(PCT)、C-反应蛋白(CRP)水平及左室射血分数(LVEF)的变化。绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC),评价血浆miRNA-497、cTnI、CK-MB对心肌损伤的诊断价值。应用Pearson相关分析法分析miRNA-497与cTnI、CK-MB、NT-proBNP、PCT、CRP及LVEF的相关性。
结果: 心肌损伤组血浆miRNA-497、cTnI、CK-MB、NT-proBNP、PCT及CRP水平均明显高于非心肌损组(P<0.05)。血浆miRNA-497、cTnI、CK-MB及三项联合诊断心肌损伤的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.918、0.931、0.775、0.940。miRNA-497的最佳阈值为2.05时,其诊断心肌损伤的敏感度和特异度较好,分别为90.4%和91.2%。相关分析显示,心肌损伤患儿血浆miRNA-497与cTnI的相关性较好(r=0.728,P<0.01)。
结论: 血浆miRNA-497对小儿脓毒症心肌损伤的诊断价值与cTnI相当,有望作为早期诊断心肌损伤的潜在标志物。
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Value of combined detection of biomarkers in early diagnosis and prognosis of patients with septic myocardial injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Apr;33(4):443-448. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210128-00158. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34053488 Chinese.
-
The Diagnostic Value of Plasma miRNA-497, cTnI, FABP3 and GPBB in Pediatric Sepsis Complicated with Myocardial Injury.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021 Jun 1;17:563-570. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S309800. eCollection 2021. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021. PMID: 34113113 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Prognostic Risk Factors of Sepsis Patients With Myocardial Injury: Six-month Survival Outcome.Altern Ther Health Med. 2023 Nov;29(8):744-749. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023. PMID: 37708545
-
[Advances in biomarkers of myocardial injury in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Jul;30(7):699-702. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.07.017. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30045802 Review. Chinese.
-
Role of Salivary Biomarkers in Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD).Proteomes. 2017 Aug 7;5(3):21. doi: 10.3390/proteomes5030021. Proteomes. 2017. PMID: 28783097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Omics Complexity in Sepsis: The Limits of the Personalized Medicine Approach.J Pers Med. 2024 Feb 20;14(3):225. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030225. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38540968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Diagnostic value of endogenous morphine in childhood sepsis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Aug;20(8):623-628. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2018.08.005. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30111470 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs on Immune Responses During Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:798713. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.798713. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Cells Activate Peripheral Natural Killer T Cells and Participate in Regulation of Downstream Immune Cascades in Patients with Sepsis.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Oct 16;24:7387-7398. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911466. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30324936 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR‑335 exerts protective effects against sepsis‑induced myocardial injury.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):806. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12446. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34542164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jayaprakash N, Gajic O, Frank RD, et al. Elevated modified shock index in early sepsis is associated with myocardial dysfunction and mortality. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883944117305683. J Crit Care. 2017;43:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Lu J, Luo Y, et al. High association between human circulating microRNA-497 and acute myocardial infarction. http://circgenetics.ahajournals.org/content/3/6/499 Sci World J. 2014:931845. - PMC - PubMed
-
- 高 戈, 冯 喆, 常 志刚, et al. 2012国际严重脓毒症及脓毒性休克诊疗指南. http://guide.medlive.cn/guidelinesub/959 中华危重病急救医学. 2013;25(8):501–505.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous