An aberrant SREBP-dependent lipogenic program promotes metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 29335545
- PMCID: PMC6714980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-017-0027-2
An aberrant SREBP-dependent lipogenic program promotes metastatic prostate cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: An aberrant SREBP-dependent lipogenic program promotes metastatic prostate cancer.Nat Genet. 2025 Nov;57(11):2931. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02394-w. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 41125873 No abstract available.
Abstract
Lipids, either endogenously synthesized or exogenous, have been linked to human cancer. Here we found that PML is frequently co-deleted with PTEN in metastatic human prostate cancer (CaP). We demonstrated that conditional inactivation of Pml in the mouse prostate morphs indolent Pten-null tumors into lethal metastatic disease. We identified MAPK reactivation, subsequent hyperactivation of an aberrant SREBP prometastatic lipogenic program, and a distinctive lipidomic profile as key characteristic features of metastatic Pml and Pten double-null CaP. Furthermore, targeting SREBP in vivo by fatostatin blocked both tumor growth and distant metastasis. Importantly, a high-fat diet (HFD) induced lipid accumulation in prostate tumors and was sufficient to drive metastasis in a nonmetastatic Pten-null mouse model of CaP, and an SREBP signature was highly enriched in metastatic human CaP. Thus, our findings uncover a prometastatic lipogenic program and lend direct genetic and experimental support to the notion that a Western HFD can promote metastasis.
Figures
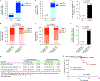
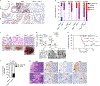



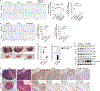

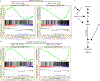
Comment in
-
Genetics of lipid metabolism in prostate cancer.Nat Genet. 2018 Feb;50(2):169-171. doi: 10.1038/s41588-017-0037-0. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 29335543 No abstract available.
-
Re: Jinjing Chen, Ilaria Guccini, Diletta Di Mitri, et al. Compartmentalized Activities of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Sustain Lipogenesis in Prostate Cancer. Nat Genet 2018;50:219-28: Lipid Metabolism in Prostate Cancer: Expanding Patient Therapeutic Opportunities.Eur Urol. 2018 Jul;74(1):e20-e21. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29598985 No abstract available.
-
Re: An Aberrant SREBP-Dependent Lipogenic Program Promotes Metastatic Prostate Cancer.J Urol. 2018 Sep;200(3):501-502. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.102. Epub 2018 May 30. J Urol. 2018. PMID: 30412986 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu JN, Fish KM, Evans CP, Devere White RW & Dall’Era MA No improvement noted in overall or cause-specific survival for men presenting with metastatic prostate cancer over a 20-year period. Cancer 120, 818–823 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Grönberg H Prostate cancer epidemiology. Lancet 361, 859–864 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Markozannes G et al. Diet, body size, physical activity and risk of prostate cancer: an umbrella review of the evidence. Eur. J. Cancer 69, 61–69 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

