Alteration in Fluidity of Cell Plasma Membrane in Huntington Disease Revealed by Spectral Phasor Analysis
- PMID: 29335600
- PMCID: PMC5768877
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19160-0
Alteration in Fluidity of Cell Plasma Membrane in Huntington Disease Revealed by Spectral Phasor Analysis
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Alteration in Fluidity of Cell Plasma Membrane in Huntington Disease Revealed by Spectral Phasor Analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 11;8(1):6060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24031-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29643420 Free PMC article.
Abstract
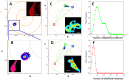
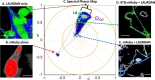
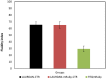
Huntington disease (HD) is a late-onset genetic neurodegenerative disorder caused by expansion of cytosine-adenine-guanine (CAG) trinucleotide in the exon 1 of the gene encoding the polyglutamine (polyQ). It has been shown that protein degradation and lipid metabolism is altered in HD. In many neurodegenerative disorders, impaired lipid homeostasis is one of the early events in the disease onset. Yet, little is known about how mutant huntingtin may affect phospholipids membrane fluidity. Here, we investigated how membrane fluidity in the living cells (differentiated PC12 and HEK293 cell lines) are affected using a hyperspectral imaging of widely used probes, LAURDAN. Using phasor approach, we characterized the fluorescence of LAURDAN that is sensitive to the polarity of the immediate environment. LAURDAN is affected by the physical order of phospholipids (lipid order) and reports the membrane fluidity. We also validated our results using a different fluorescent membrane probe, Nile Red (NR). The plasma membrane in the cells expressing expanded polyQ shows a shift toward increased membrane fluidity revealed by both LAURDAN and NR spectral phasors. This finding brings a new perspective in the understanding of the early stages of HD that can be used as a target for drug screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

