The new genetics of intelligence
- PMID: 29335645
- PMCID: PMC5985927
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg.2017.104
The new genetics of intelligence
Abstract
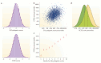
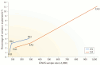
Intelligence - the ability to learn, reason and solve problems - is at the forefront of behavioural genetic research. Intelligence is highly heritable and predicts important educational, occupational and health outcomes better than any other trait. Recent genome-wide association studies have successfully identified inherited genome sequence differences that account for 20% of the 50% heritability of intelligence. These findings open new avenues for research into the causes and consequences of intelligence using genome-wide polygenic scores that aggregate the effects of thousands of genetic variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gottfredson LS. Why g matters: The complexity of everyday life. Intelligence. 1997;24:79–132.
-
- Deary IJ, et al. Genetic contributions to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age. Nature. 2012;482:212–214. - PubMed
-
- Deary IJ, Strand S, Smith P, Fernandes C. Intelligence and educational achievement. Intelligence. 2007;35:13–21.
-
- Schmidt FL, Hunter J. General mental ability in the world of work: occupational attainment and job performance. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;86:162–173. - PubMed
-
- Strenze T. Intelligence and socioeconomic success: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal research. Intelligence. 2007;35:401–426.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

