Effectiveness of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor as an Add-on Drug to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Glycemic Control of a Patient with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Case Report
- PMID: 29335890
- PMCID: PMC5801255
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-018-0369-5
Effectiveness of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor as an Add-on Drug to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Glycemic Control of a Patient with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes patients with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) are obese because of hyperphagia; weight control by dietary modification and medicine is required for glycemic control. There are several recent reports showing the effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) for diabetes treatment in PWS.
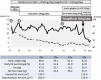
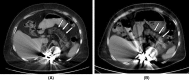
Case report: A 36-year-old Japanese male patient was diagnosed with PWS at 10 years of age. At age 16 years, he was diagnosed with diabetes and began to take several kinds of oral hypoglycemic agents. At age 29 years, his BMI was 39.1 kg/m2 and he was referred to our department for diabetes and obesity treatment. In the present case, the HbA1c was not improved by GLP-1RAs despite a 28-kg BW reduction, which included a 9-kg loss of muscle. Apprehensive of further loss of muscle mass, basal insulin of insulin glargine was administered in addition to GLP-1RAs. Immediately after the addition of tofogliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, the patient's HbA1c decreased dramatically with only about an additional 3% BW reduction. We note an improvement in our case of lipid deposition in the pancreas confirmed by abdominal CT after the improvement of HbA1c. It is unknown whether this improvement of fatty pancreas was a cause or an effect of the improved glycemic control in the present case.
Conclusion: This finding clearly supports the effectiveness of combining SGLT2 inhibitors with GLP-1RAs for treatment of patients with PWS and non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs); Non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD); Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS); Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist for the glycemic control of a patient with Prader-Willi syndrome: a case report.Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020;29(2):81-84. doi: 10.1297/cpe.29.81. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32313377 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in glycaemic parameters using SGLT-2 inhibitor and GLP-1 agonist in combination in an adolescent with diabetes mellitus and Prader-Willi syndrome: a case report.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul 28;33(7):951-955. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0389. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32447330
-
How Do SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) Inhibitors and GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) Receptor Agonists Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes?: Completed and Ongoing Mechanistic Trials.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Mar;40(3):506-522. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.311904. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31996025 Review.
-
The effects of glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 receptor agonists on weight and glycaemic control in Prader-Willi syndrome: A systematic review.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022 Feb;96(2):144-154. doi: 10.1111/cen.14583. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 34448208
-
Treatment Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes with Obesity: Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists.Clin Ther. 2017 Jun;39(6):1244-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 May 16. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28526416 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist for the glycemic control of a patient with Prader-Willi syndrome: a case report.Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020;29(2):81-84. doi: 10.1297/cpe.29.81. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32313377 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy in a young subject with Prader-Willi syndrome, obesity, and type 2 diabetes: a case report.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 10;16:1533209. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1533209. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39996062 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Natural History during the Transition from Childhood to Adulthood in a Cohort of 39 Patients.J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 15;10(22):5310. doi: 10.3390/jcm10225310. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34830599 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney disease in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome: international cohort study and systematic literature review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 21;14:1168648. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1168648. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37547314 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine features of Prader-Willi syndrome: a narrative review focusing on genotype-phenotype correlation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 26;15:1382583. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1382583. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38737552 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

