Gefitinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29336009
- PMCID: PMC6491254
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006847.pub2
Gefitinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The role of gefitinib for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is evolving. We undertook a systematic review to evaluate the available evidence from all randomised trials.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and safety of gefitinib as first-line, second-line or maintenance treatment for advanced NSCLC.
Search methods: We performed searches in CENTRAL, MEDLINE and Embase from inception to 17 February 2017. We handsearched relevant conference proceedings, clinical trial registries and references lists of retrieved articles.
Selection criteria: We included trials assessing gefitinib, alone or in combination with other treatment, compared to placebo or other treatments in the first- or successive-line treatment of patients with NSCLC, excluding compassionate use.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard Cochrane methodology. Two authors independently assessed the search results to select those with sound methodological quality. We carried out all analyses on an intention-to-treat basis. We recorded the following outcome data: overall survival, progression-free survival, toxicity, tumour response and quality of life. We also collected data for the following subgroups: Asian ethnicity and positive epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation.
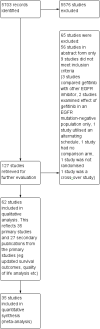
Main results: We included 35 eligible randomised controlled trials (RCTs), which examined 12,089 patients.General populationGefitinib did not statistically improve overall survival when compared with placebo or chemotherapy in either first- or second-line settings. Second-line gefitinib prolonged time to treatment failure (TTF) (hazard ratio (HR) 0.82, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.75 to 0.90, P < 0.0001) when compared with placebo. Maintenance gefitinib improved progression-free survival (HR 0.70, 95% CI 0.53 to 0.91, P = 0.007) after first-line therapy.Studies in patients of Asian ethnicity or that conducted subgroup analysesSecond-line gefitinib prolonged overall survival over placebo (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.91, P = 0.01). In the first-line setting, progression-free survival was improved with gefitinib over chemotherapy alone (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.98, P = 0.04, moderate quality of evidence). Gefitinib given in combination with a chemotherapy regimen improved progression-free survival versus either gefitinib alone or chemotherapy alone (HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.49 to 0.96, P = 0.03; HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.77, P < 0.00001, respectively). In the second-line setting, progression-free survival was superior in patients given gefitinib over placebo or chemotherapy (HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.52 to 0.91, P = 0.009; HR 0.71, 95% CI 0.57 to 0.88, P = 0.002; moderate quality of evidence, respectively). Combining gefitinib with chemotherapy in the second-line setting was superior to gefitinib alone (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.97, P = 0.04). As maintenance therapy, gefitinib improved progression-free survival when compared with placebo (HR 0.42, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.54, P < 0.00001).Patients with EGFR mutation-positive tumoursStudies in patients with EGFR mutation-positive tumours showed an improvement in progression-free survival in favour of gefitinib over first-line and second-line chemotherapy (HR 0.47, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.61, P < 0.00001; HR 0.24, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.47, P < 0.0001, respectively). Gefitinib as maintenance therapy following chemotherapy improved overall and progression-free survival (HR 0.39, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.98, P = 0.05; HR 0.17, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.41, P < 0.0001, respectively) in one phase III study when compared to placebo.Toxicities from gefitinib included skin rash, diarrhoea and liver transaminase derangements. Toxicities from chemotherapy included anaemia, neutropenia and neurotoxicity.In terms of quality of life, gefitinib improved Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Lung (FACT-L) (standardised mean difference (SMD) 10.50, 95% CI 9.55 to 11.45, P < 0.000001), lung cancer subscale (SMD 3.63, 95% CI 3.08 to 4.19, P < 0.00001) and Trial Outcome Index (SMD 9.87, 95% CI 1.26 to 18.48, P < 0.00001) scores when compared with chemotherapy.
Authors' conclusions: This systematic review shows that gefitinib, when compared with standard first- or second-line chemotherapy or maintenance therapy, probably has a beneficial effect on progression-free survival and quality of life in selected patient populations, particularly those with tumours bearing sensitising EGFR mutations.Patients with EGFR mutations lived longer when given maintenance gefitinib than those given placebo.One study conducted subgroup analysis and showed that gefitinib improved overall survival over placebo in the second-line setting in patients of Asian ethnicity. All other studies did not detect any benefit on overall survival. The data analysed in this review were very heterogenous. We were limited in the amount of data that could be pooled, largely due to variations in study design. The risk of bias in most studies was moderate, with some studies not adequately addressing potential selection, attrition and reporting bias. This heterogeneity may have an impact on the applicability of the resultsCombining gefitinib with chemotherapy appears to be superior in improving progression-free survival to either gefitinib or chemotherapy alone, however further data and phase III studies in these settings are required.Gefitinib has a favourable toxicity profile when compared with current chemotherapy regimens. Although there is no improvement in overall survival, gefitinib compares favourably with cytotoxic chemotherapy in patients with EGFR mutations with a prolongation of progression-free survival and a lesser side effect profile.
Conflict of interest statement
Esther HA Sim (ES): none known
Ian A Yang (IY): none known
Rayleen V Bowman (RB) has received pharmaceutical company sponsored items, meals and travel expenses associated with attendance at scientific meetings including Australian Lung Cancer Conference and Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. RB is a current member of the Lung Foundation (Australia)'s Lung Cancer Consultative Group, which receives financial sponsorship from a number of pharmaceutical companies.
Kwun M Fong (KF) was an investigator for a clinical trial of gefitinib for lung cancer (Astra Zeneca international trial) ‐ funding received by the Hospital funds the clinical trial and the employment of a trials nurse. KF's laboratory has also undertaken contract research for a clinical study looking at immunohistochemistry of certain proteins in lung cancer for Novartis ‐ funding received will go to the Project and employment of Research staff for the Project. KF was previously offered an honorarium from a pharmaceutical company for attending an one‐off Advisory Board Meeting; this was not accepted and asked to be given to a charity. KF has received occasional pens, pads and minor stationery from industry. KF has occasionally attended/spoken at meetings organised by pharmaceutical companies where meals/travel costs would be sponsored. KF has organised the Queensland Lung Cancer Interest Group Meeting (two to three meetings per year, a teleconference meeting, which is supported by Eli Lilly. KF has/is also involved in organising and attending professional meetings including those run by the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand, Asia‐Pacific Society of Respirology, Australian Lung Cancer Conference, IASLC, where some sponsorship is usually provided by industry. KF is involved with the Lung Foundation (Australia)'s Lung Cancer Cooperative Group (not‐for‐profit, public benevolent institution) (http://www.lungnet.org/www.lungnet.org.au) and its activities, which includes promotion of Cochrane Reviews. The LFA receives support from pharmaceutical companies. KF was Chair of the Australian Lung Cancer trials Group, which receives some support funding from pharmaceutical companies.
Richard Wood‐Baker (RWB): none known
Figures





Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahn 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ahn MJ, Yang JCH, Liang J, Kang JH, Xiu Q, Chen YM, et al. Randomized phase II trial of first‐line treatment with pemetrexed‐cisplatin, followed sequentially by gefitinib or pemetrexed, in East Asian, never‐smoker patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2012;77:346‐52. - PubMed
An 2016 {published data only}
-
- An C, Zhang J, Chu H, Gu C, Xiao F, Zhu F, et al. Study of gefitinib and pemetrexed as first‐line treatment in patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutation. Pathology and Oncology Research 2016;22:763‐8. - PubMed
Chen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chen YM, Liu JM, Chou TY, Perng RP, Tsai CM, Whang‐Peng J. Phase II randomized study of daily gefitinib treatment alone or with vinorelbine every 2 weeks in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung who failed at least 2 regimens of chemotherapy. Cancer 2007;109(9):1821‐8. - PubMed
Chen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chen YM, Fan WC, Tsai CM, Liu SH, Shih JF, Chou TY, et al. A phase II randomized trial of gefitinib alone or with Tegafur/uracil treatment in patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma who had failed previous chemotherapy. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2011;6:1110‐6. - PubMed
Cheng 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cheng Y, Murakami H, Yang PC, He J, Nakagawa K, Kang JH, et al. Randomized phase II trial of gefitinib with and without pemetrexed as first‐line therapy in patients with advanced nonsquamous non‐small‐cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;27(20):3258‐66. - PubMed
Crino 2008 INVITE {published data only}
-
- Crino L, Cappuzzo F, Zatloukal P, Reck M, Pesek M, Thompson JC, et al. Gefitinib versus vinorelbine in chemotherapy‐naive elderly patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (INVITE): a randomized, phase II study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(26):4253‐60. - PubMed
Cufer 2006 SIGN {published data only}
-
- Cufer T, Vrdoljak E, Gaafar R, Erensoy I, Pemberton K, SIGN study group. Phase II, open‐label, randomized study (SIGN) or single‐agent gefitinib (IRESSA) or docetaxel as second‐line therapy in patients with advanced (stage IIIb or IV) non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2006;17(4):401‐9. - PubMed
Dai 2013 {published data only}
Fukuoka 2003 IDEAL I {published data only}
-
- Baelga J, Kris M, Yano S, Natale R, Giaccone G, Brahmer J, et al. Phase II trials (IDEAL 1 and IDEAL 2) of ZD1839 in advanced or metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient. Annals of Oncology 2002;13(Suppl 5):131 Abs 481.
-
- Douillard JY, Giaccone G, Horai T, Noda K, Vansteenkiste JF, Takata I, et al. Improvement in disease‐related symptoms and quality of life in patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with ZD1839 ('Iressa') (IDEAL 1) [abstract]. 38th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology; 18‐21 May 2002; Orlando, Florida, USA. 2002; Vol. 21 Pt 1:299a, Abs 1195.
-
- Douillard JY, Skarin A, Baselga J, Natale R, Giaccone G, Maddox AM, et al. Improvement in disease‐related symptoms and quality of life (QOL) for advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with ZD1839 in IDEAL 1 and IDEAL 2. Annals of Oncology 2002;13 Suppl 5:131, Abs 480.
-
- Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, et al. Multi‐institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2003;21(12):2237‐46. - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al. [Final results from a phase II trial of ZD1839 ('Iressa') for patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (IDEAL 1) [abstract]]. 38th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology; 18‐21 May 2002; Orlando, Florida, USA. 2002; Vol. 21 Pt 1:298a, Abs 1188.
Gaafar 2011 EORTC08021 {published data only}
-
- Gaafar R M, Surmont V, Scagliotti G, Klaveren R, Papamichael D, Welch J, et al. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled phase III intergroup study of gefitinib (G) in patients (pts) with advanced NSCLC, non‐progressing after first‐line platinum‐based chemotherapy (EORTC 08021‐ILCP 01/03). 2010 Annual Meeting of the Americal Society of CLinical Oncology, ASCO, Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2010; Vol. 28.
-
- Gaafar RM, Surmont VF, Scagliotti GV, Klaveren RJ, Papamichael D, Welch JJ, et al. A double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled phase III intergroup study of gefitinib in patients with advanced NSCLC, non‐progressing after first line platinum‐based chemotherapy (EORTC 08021/ILCP 01/03). European Journal of Cancer 2011;47:2331‐40. - PubMed
-
- Surmont VF, Gaafar RM, Scagliotti GV, Klaveren RJ, Papamichael D, Hasan B, et al. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled phase III study of gefitinib (G) versus placebo (P) in patients (pts) with advanced NSCLC, non progressing after first‐line platinum‐based chemotherapy (EORTC 08021‐ ILCP). 35th ESMO Congress Milan Italy. Oxford University Press, 2010; Vol. 21:viii124.
Giaccone 2004 INTACT I {published data only}
-
- Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Maserlat SM, Harris PL, Okimoto FA, Brannigan BW, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non‐small‐cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(31):8081‐92. - PubMed
-
- Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer: a phase III trial ‐ INTACT I. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2004;22(5):777‐84. - PubMed
-
- Giaccone G, Johnson DH, Manegold C, et al. A phase III clinical trial of ZD1839 ('Iressa') in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in chemotherapy‐naive patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (INTACT 1). Annals of Oncology 2002;13 Suppl 5:2, Abstract 4.
Goss 2009 INSTEP {published data only}
Han 2012 First SIGNAL {published data only}
-
- Han JY, Park K, Kim SW, Lee DH, Kim HY, Kim HT, et al. First‐SIGNAL: first‐line single‐agent Iressa versus gemcitabine and cisplatin trial in never‐smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012;30:1122‐8. - PubMed
-
- Han JY, Yoon KA, Park JH, Lee YJ, Lee GK, Han JH, et al. DNA repair gene polymorphisms and benefit from gefitinib in never‐smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2011;117(14):3201‐8. - PubMed
Herbst 2004 INTACT II {published data only}
-
- Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, Natale RB, Miller V, Manegold C, et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer: a phase III trial ‐ INTACT 2. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2004;22(5):785‐94. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DH, Herbst R, Giaccone G, et al. ZD1839 ('Iressa') in combination with paclitaxel & carboplatin in chemotherapy‐naive patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): results from a phase III clinical trial (INTACT 2). Annals of Oncology 2002;13 Suppl 5:127, Abstract 468.
Kelly 2008 SWOG S0023 {published data only}
-
- Kelly K, Chansky K, Gaspar LE, Albain KS, Jett J, Ung YC, et al. Phase III trial of maintenance gefitinib or placebo after concurrent chemoradiotherapy and docetaxel consolidation in inoperable stage III non‐small‐cell lung cancer: SWOG S0023. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(15):2450‐6. [SWOG S0023] - PubMed
-
- Kelly K, Gaspar LE, Chansky K, Albain KS, Crowley J, Gandara DR. Low incidence of pneumonitis on SWOG 0023: A preliminary analysis of an ongoing phase III trial of concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by consolidation docetaxel and Iressa/placebo maintenance in patients with inoperable stage III non‐small cell lung cancer [abstract]. 41st Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Orlando, FL, 13‐17 May, 2005 (Abstract No. 7058). 2005; Vol. 23:634.
Kim 2008 INTEREST {published data only}
-
- Douillard JY, Shephard FA, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, et al. Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib and docetaxel in previously treated non‐small‐cell lung cancer: from the randomized phase III INTEREST Trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(5):744‐52. - PubMed
-
- Horgan AM, Bradbury PA, Amir E, Ng R, Douillard JY, Kim ES, et al. An economic analysis of the INTEREST trial, a randomized trial of docetaxel versus gefitinib as second‐/third‐line therapy in advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Annals of Oncology. United Kingdom: Oxford University Press (Great Clarendon Street, Oxford OX2 6DP, United Kingdom), 2011; Vol. 22:1805‐11. - PubMed
-
- Horgan AM, Shepherd FA, Bradbury PA, Ng R, Leighl NB. Preliminary cost‐consequence analysis of the INTEREST trial, a randomized trial of docetaxel versus gefitinib as 2nd line therapy in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer [abstract no. 8110]. Journal of Clinical Oncology: ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2008;25(15 Suppl Pt 1):451.
-
- Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, Wu YL, et al. Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non‐small‐cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomized phase III trial. Lancet 2008;372:1809‐18. - PubMed
Kim 2016 {published data only}
Kris 2003 IDEAL II {published data only}
-
- Cella D, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, et al. Clinically meaningful improvement in symptoms and quality of life for patients with non‐small cell lung cancer receiving gefitinib in a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(13):2946‐54. - PubMed
-
- Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, et al. A phase II trial of ZD1839 ('Iressa') in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who had failed platinum‐ and docetaxel‐based regimens (IDEAL 2) [abstract]. 38th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology; 18‐21 May 2002; Orlando, Florida, USA. 2002; Vol. 21 Pt 1:292a Abstract 1166.
-
- Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non‐small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003;290(16):2149‐58. - PubMed
-
- Natale RB, Skarin A, Maddox AM, et al. Improvement in symptoms and quality of life for advanced non‐small cell lung cancer patients receiving ZD1839 ('Iressa') in IDEAL 2 [abstract]. 38th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology; 18‐21 May 2002; Orlando, Florida, USA. 2002; Vol. 21 Pt 1:292a, Abstract 1167.
Lee 2010 ISTANA {published data only}
-
- Lee D, Kim S, Park K, et al. A randomized open‐label study of gefitinib versus docetaxel in patients with advanced/metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have previously received platinum‐based chemotherapy [abstract no. 8025]. Journal of Clinical Oncology: ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2008;26(15 Suppl Pt I):430.
-
- Lee DH, Park K, Kim JH, Lee JS, Shin SW, Kang JH, et al. Randomized phase III trial of gefitinib versus docetaxel in non‐small‐cell lung cancer patients who have previously received platinum‐based chemotherapy. Clinical Cancer Research 2010;16(4):1307‐14. [ISTANA] - PubMed
Li 2010 {published data only}
-
- Li H, Wang X, Hua F. Second‐line treatment with gefitinib or docetaxel for advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;37:16‐8.
Lou 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lou N, Yang J, Yan H, Qing Z, Liao R, Xu C, et al. Efficacies of gefitinib versus paclitaxel/carboplatin for patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma. National Medical Journal of China 2014;94(30):2337‐41. - PubMed
Maemondo 2010 NEJ002 {published data only}
-
- Fukuhara T, Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, et al. Factors associated with a poor response to gefitinib in the NEJ002 study: smoking and the L858R mutation. Lung Cancer 2015;88:181‐6. - PubMed
-
- Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib with carboplatin‐paclitaxel for chemo‐naive non‐small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations (NEJ002). Annals of Oncology. United Kingdom: Oxford University Press (Great Clarendon Street, Oxford OX2 6DP, United Kingdom), 2013; Vol. 24:54‐9. - PubMed
-
- Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, et al. A randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib with carboplatin (CBDCA) plus paclitaxel (TXL) for the first‐line treatment of non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with sensitive EGFR mutations: NEJ002 study. European Journal of Cancer. 2009:Abstract 9LBA.
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;362(25):2380‐8. - PubMed
-
- Miyauchi E, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, et al. Efficacy of chemotherapy after first‐line gefitinib therapy in EGFR mutation‐positive advanced non‐small cell lung cancer ‐ data from a randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib with carboplatin plus paclitaxel (NEJ002). Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;45(7):670‐6. - PubMed
Maruyama 2008 V‐15‐32 {published data only}
-
- Leki R, Kawahara M, Watanabe H, et al. The impact of response evaluation committee in a Phase III study (V‐15‐32) of gefitinib versus docetaxel in Japanese patients with non‐small cell lung cancer [Abstract No. 298P]. Annals of Oncology 2009;19 Suppl 8:109‐10.
-
- Maruyama R, Nishiwaki Y, Tamura T, Yamamoto N, Tsuboi M, Nakagawa K, et al. Phase III study, V‐15‐32, of gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated Japanese patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(26):4245‐52. - PubMed
-
- Sekine I, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Yamamoto N, Tsuboi M, Nakagawa K, et al. Quality of life and disease‐related symptoms in previously treated Japanese patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer: results of a randomized phase III study (V‐15‐32) of gefitinib versus docetaxel. Annals of Oncology 2009;20(9):1483‐8. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto N, Nishiwaki Y, Negoro S, Jiang H, Itoh Y, Saijo N, et al. Disease control as a predictor of survival with gefitinib and docetaxel in a phase III study (V‐15‐32) in advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer patients. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2010;5(7):1042‐7. - PubMed
Mitsudomi 2010 WJTOG3405 {published data only}
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Seto T, et al. Updated overall survival results of WJTOG 3405, a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib (G) with cisplatin plus docetaxel (CD) as the first‐line treatment for patients with non‐small cell lung cancer harboring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). 2012 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, ASCO Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2012; Vol. 30.
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase III trial. Lancet 2010;11:121‐8. - PubMed
-
- Tsurutani J, Mitsudomi T, Mori S, Okamoto I, Nozaki K, Tada H, et al. A phase III, first‐line trial of gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel for patients with advanced or recurrent non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring activating mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene: a preliminary results of WJTOG 3405 [abstract O‐9002]. European Journal of Cancer. 2009; Vol. 7 Suppl:505.
Mok 2009 IPASS {published data only}
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open‐label, first‐line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non ‐ small‐cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29:2866‐74. - PubMed
-
- Mok T, Wu Y‐L, Thongprasert S, et al. Phase III, randomised, open‐label, first‐line study of gefitinib (G) vs carboplatin/paclitaxel (C/P) in clinically selected patients (PTS) with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (IPASS). Annals of Oncology 2008;19 Suppl 8:Viii1.
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin‐paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(10):947‐57. - PubMed
-
- Ohe Y, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, et al. Phase III, randomized, open‐label, first‐line study of gefitinib (G) versus carboplatin/paclitaxel (C/P) in selected patients (pts) with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (IPASS): Evaluation of recruits in Japan. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;29(15 Suppl 1):8044.
-
- Thongprasert S, Duffield E, Saijo N, Wu YL, Yang JC, Chu DT, et al. Health‐related quality‐of‐life in a randomized phase III first‐line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients from Asia with advanced NSCLC (IPASS). Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2011;6:1872‐80. - PubMed
Morere 2010 IFCT‐0301 {published data only}
-
- Guetz G, Landre T, Westeel V, Milleron B, Vaylet F, Urban T, et al. Similar survival rates with first‐line gefitinib, gemcitabine or docetaxel in a randomized phase II trial in elderly patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer and a poor performance status (IFCT‐0301). Journal of Geriatric Oncology 2015;6:233‐40. - PubMed
-
- Morere J, Westeel V, Morin F, et al. Randomized phase II trial of first‐line gefitinib,gemcitabine or docetaxel in performance status (PS) 2 or 3 non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (IFCT‐0301) [abstract no. 8086]. Journal of Clinical Oncology: ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2008;26(15 Suppl Pt I):445.
-
- Morere JF, Brechot JM, Westeel V, Gounant V, Lebeau B, Vaylet F, et al. Randomized phase II trial of gefitinib or gemcitabine or docetaxel chemotherapy in patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer and a performance status of 2 or 3 (IFCT‐0301 study). Lung Cancer 2010;70(1):301‐7. - PubMed
Soria 2015 IMPRESS {published data only}
-
- Soria JC, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Kim SW, Yang JJ, Ahn MJ, et al. Gefitinib plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in EGFR‐mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer after progression on first‐line gefitinib (IMPRESS): a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncology 2015;16:990‐8. - PubMed
Sun 2012 KCSG‐LU08‐01 {published data only}
-
- Ahn M, Sun J, Ahn JS, Kim S, Min YJ, Yun HJ, et al. Randomized phase III trial of gefitinib or pemetrexed as second‐line treatment in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum‐based chemotherapy (KCSG‐LU08‐01). ASCO Annual Meeting 2011 Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2011; Vol. 29.
-
- Ahn MJ, Sun JM, Lee KH, Ahn JS, Kim SW, Min YJ, et al. Randomized phase III trial of gefitinib or pemetrexed as second‐line treatment in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum‐based chemotherapy (KCSG‐LU08‐01). 14th World Conference on Lung Cancer Amsterdam Netherlands. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2011; Vol. 6:S317.
-
- Sun JM, Lee KH, Kim SW, Lee DH, Min YJ, Yun HJ, et al. Gefitinib versus pemetrexed as second‐line treatment in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum‐based chemotherapy (KCSG‐LU08‐01): an open‐label, phase 3 trial. Cancer 2012;118:6234‐42. - PubMed
Takeda 2010 WJTOG0203 {published data only}
-
- Okamoto I, Hida T, Kashii T, et al. Randomized phase III study of platinum‐doublet chemotherapy followed by gefitinib versus continued platinum‐doublet chemotherapy in patients (pts) with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Results of West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group Trial (WJTOG0203) [Abstract No. 2 33PD]. Annals of Oncology 2008;19 Suppl 8:91.
-
- Takeda K, Hida T, Sato T, Ando M, Seto T, Satouchi M, et al. Randomized phase III trial of platinum‐doublet chemotherapy followed by gefitinib comparted with continued platinum‐doublet chemotherapy in Japanese patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer: results of a West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group Trial (WJTOG0203). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(5):753‐60. - PubMed
Thatcher 2005 ISEL {published data only}
-
- Chang A, Parikh P, Thongprasert S, Tan EH, Perng RP, Ganzon D, et al. Gefitinib (IRESSA) in patients of Asian origin with refractory advanced non‐small cell lung cancer: subset analysis from the ISEL study. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2006;1(8):847‐55. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Dziadziuszko R, Thatcher N, Mann H, Watkins C, Parums DV, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor immunohistochemistry: comparison of antibodies and cutoff points to predict benefit from gefitinib in a phase 3 placebo‐controlled study in advanced non small‐cell lung cancer. Cancer 2008;112(5):1114‐21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Varella‐Garcia M, Bunn Jr PA, Franklin WA, Dziadziuszko R, Thatcher N, et al. Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib in a phase III placebo‐controlled study in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006;24(31):5034‐42. - PubMed
-
- Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Pawel J, et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer: results from a randomised, placebo‐controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet 2005;366(9496):1527‐37. - PubMed
Xu 2015 {published data only}
Xue 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Xue C, Li N, Feng W, Jia J, Peng J, et al. Randomized, open‐label, multi‐center study of gefitinib dose‐escalation (500mg/d versus 250mg/d) in advanced NSCLC patient achieved stable disease (SD) after one‐month gefitinib treatment. 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer Sydney, NSW Australia. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2013; Vol. 8:S1185.
Yang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Boye M, Wang X, Srimuninnimit V, Kang JH, Tsai CM, Orlando M, et al. First‐line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance therapy versus gefitinib monotherapy in East Asian never‐smoker patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non‐small cell lung cancer: quality of life results from a randomized phase III trial. Clinical Lung Cancer 2016;17(2):150‐60. - PubMed
-
- Kang JH, Ahn M, Kim D, Cho EK, Kim J, Shin SW, et al. Tolerability and outcomes of first‐line pemetrexed‐cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance therapy versus gefitinib monotherapy in Korean patients with advanced non‐squamous non‐small cell lung cancer: a post hoc descriptive subgroup analysis of a randomized, phase 3 trial. Cancer Research and Treatment 2015;48(2):458‐64. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Kang JH, Mok T, Ahn M, Srimuninnimit V, Lin C, et al. First‐line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance therapy versus gefitinib monotherapy in East Asian patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐squamous non‐small cell lung cancer: a randomised, phase 3 trial. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50:2219‐30. - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Park K, Mok TSK, Kang JH, Srimuninnimit V, Lin CC, et al. A randomized phase 3 study comparing first‐line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib as maintenance with gefitinib monotherapy in east Asian patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non‐small cell lung cancer (NSQNSCLC). 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer Sydney, NSW Australia. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2013; Vol. 8:S288.
-
- Yang JC, Srimuninnimit V, Ahn M, Lin C, Kim S, Tsai C, et al. A randomized phase 3 study comparing first‐line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance (PC/G) with gefitinib monotherapy (G) in East Asian patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non‐small cell lung cancer (nSqNSCLC): final survival results. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;15 Suppl:8041.
Yu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yu H, Zhang J, Wu X, Luo Z, Wang H, Sun S, et al. A phase II randomized trial evaluating gefitinib intercalated with pemetrexed/platinum chemotherapy or pemetrexed/platinum chemotherapy alone in unselected patients with advanced non‐squamous non‐small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biology and Therapy 2014;15(7):832‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Zhang 2012 INFORM {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Ma S, Song X, Han B, Cheng Y, Huang C, et al. Gefitinib versus placebo as maintenance therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer (INFORM; C‐TONG 0804): a multicentre, double‐blind randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncology 2012;13:466‐75. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Ma SL, Song XQ, Cheng Y, Huang C, Yang SJ, et al. Pre‐planned subgroup analyses from the phase III, randomised, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study of gefitinib (G) as maintenance therapy in patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (INFORM; C‐TONG 0804). European Multidisciplinary Cancer Congress Stockholm Sweden. Elsevier Ltd, 2011; Vol. 47:S622‐3.
-
- Zhang L, Ma SL, Song XQ, Han BH, Cheng Y, Huang C, et al. Efficacy, tolerability and biomarker analyses from a phase III, randomized, placebo controlled, parallel group study of gefitinib as maintenance therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in China (INFORM) (C‐TONG 0804). 14th World Conference on Lung Cancer Amsterdam Netherlands. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2011; Vol. 6:S558‐9.
-
- Zhang L, Shenglin M, Song X, Han B, Cheng Y, Huang C, et al. Efficacy, tolerability, and biomarker analyses from a phase III, randomized, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study of gefitinib as maintenance therapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC; INFORM; C‐TONG 0804). ASCO Annual Meeting 2011 Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2011; Vol. 29.
References to studies excluded from this review
Choi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Choi YJ, Lee DH, Choi CM, Lee JS, Lee SJ, Ahn J, et al. Randomized phase II study of paclitaxel/carboplatin intercalated with gefitinib compared to paclitaxel/carboplatin alone for chemotherapy‐naive non‐small cell lung cancer in a clinically selected population excluding patients with non‐smoking adenocarcinoma or mutated EGFR. BMC Cancer 2015;15:763. - PMC - PubMed
Kim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kim ST, Uhm JE, Lee J, Sun JM, Sohn I, Kim SW, et al. Randomized phase II study of gefitinib versus erlotinib in patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer who failed previous chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2012;75:82‐8. - PubMed
Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lee KH, Lee KY, Jeon YJ, et al. A phase IV, multicenter, non‐randomized, open‐labelled study to evaluate the efficacy of gefitinib (Iressa®) as a second‐line therapy in Korean patients with non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Respirology. 2009; Vol. 14 Suppl S3:A161.
Manegold 2005 {published data only}
-
- Manegold C, Gatzemeier U, Buchholz E, Smith RP, Fandi A. A pilot trial of gefitinib in combination with docetaxel in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Clinical Lung Cancer 2005;6(6):343‐9. - PubMed
Natale 2009 {published data only}
-
- Natale RB, Bodkin D, Govindan R, Sleckman BG, Rizvi NA, Capo A, et al. Vandetanib versus gefitinib in patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer: results from a two‐part, double‐blind, randomized phase II study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;27(15):2523‐9. - PubMed
Shi 2013 ICOGEN {published data only}
-
- Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou C, Zhang L, Zhang S, et al. Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (ICOGEN): a randomised, double‐blind phase 3 non‐inferiority trial. Lancet Oncology 2013;14:953‐61. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou C, Li Z, et al. Final overall survival and updated biomarker analysis results from the randomized phase III ICOGEN trial. 2012 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, ASCO Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2012; Vol. 30.
-
- Sun Y, Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou C, Wang D, et al. A randomized, doubleblind phase III study of icotinib versus gefitinib in patients with advanced non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) previously treated with chemotherapy (ICOGEN). 14th World Conference on Lung Cancer Amsterdam Netherlands. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2011; Vol. 6:S317‐8.
Sugawara 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Minato K, Harada T, Inoue A, Fujita Y, et al. Randomized phase II study of concurrent versus sequential alternating gefitinib and chemotherapy in previously untreated non‐small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR mutations: NEJ005/TCOG0902. Annals of Oncology 2015;26:888‐94. - PubMed
Urata 2016 {published data only}
-
- Urata Y, Katakami N, Morita S, Kaji R, Yoshioka H, Seto T, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib with erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced lung adenocarcinoma: WJOG 5108L. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(27):3248‐57. - PubMed
Zhou 2014 CTONG 0806 {published data only}
-
- Yang J, Cheng Y, Zhao M, Zhou Q, Yan HH, Zhang L, et al. A phase II trial comparing pemetrexed with gefitinib as the second‐line treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC patients with wild‐type EGFR (CTONG0806). 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, ASCO Chicago, IL United States. American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2013; Vol. 31.
-
- Zhou Q, Cheng Y, Yang JJ, Zhao MF, Zhang L, Zhang XC, et al. Pemetrexed versus gefitinib as second‐line treatment in advanced non‐squamous nonsmall‐cell lung cancer patients harbouring wild‐type EGFR (CTONG 0806): a multicenter randomized trial. Annals of Oncology 2014;25(12):2385‐91. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Q, Cheng Y, Zhao MF, Yang JJ, Yan H H, Zhang L, et al. Final results of CTONG 0806: a phase II trial comparing pemetrexed with gefitinib as second‐line treatment of advanced non‐squamous NSCLC patients with wild‐type EGFR. 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer Sydney, NSW Australia. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2013; Vol. 8:S194‐5.
References to ongoing studies
Bhatnagar 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bhatnagar AR, Singh DP, Sharma R, Kumbhaj P. Docetaxel versus geftinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC pretreated with platinum‐based chemotherapy. 4th Australian Lung Cancer Conference, ALCC 2012 Adelaide, SA Australia. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2012; Vol. 7:S159.
Gaafar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gaafar RM, Surmont V, Scagliotti G, Klaveren R, Papamichael G, Welch J, et al. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled phase III intergroup study of gefitinib (G) in patients (pts) with advanced NSCLC, non‐progressing after first‐line platinum‐based chemotherapy (EORTC 08021‐ILCP 01/03). Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2010; Vol. 28 Suppl 15.
Hong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hong J, Kyung SY, Lee SP, Park JW, Jung SH, Sym SJ, et al. Randomized phase II study of pemetrexed versus gefitinib for patients with previously treated non‐small cell lung cancer. 4th Asia Pacific Lung Cancer Conference, APLCC 2010 Seoul, South Korea. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2010; Vol. 5:S401.
Laurie 2000 {published data only}
-
- Laurie SA, Miller VA, Johnson D, Ng KK, Heelan RT, Pizzo BA, et al. Pilot trial of ZD1839 (Iressa‐TM‐), an oral inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase, in combination with carboplatin (C) and paclitaxel (P) in previously untreated advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2000; Vol. 29 Suppl 1:S71.
Lee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lee DH, Kim JE, Choi YJ, Choi CM, Lee JS, Kim SW. Randomized phase II study comparing paclitaxel/carboplatin intercalated with gefitinib to paclitaxel/carboplatin alone for chemotherapy‐naive non‐small cell lung cancer patients either with history of smoking or with wild‐type EGFR. AACR‐NCI‐EORTC International Conference: Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics 2013 Boston, MA United States. American Association for Cancer Research Inc, 2013; Vol. 12.
Liang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liang J, Ahn M, Kang J, et al. First‐line treatment (txt) with pemetrexed‐cisplatin (PC), followed sequentially by gefitinib (G) or pemetrexed, in Asian, never‐smoker (n/smkr) patients (pts) with advanced NSCLC: An open‐label, randomized phase II trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(15 Suppl 1):Abstract 7591.
Nokihara 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nokihara H, Ohe Y, Kawaishi M, et al. A randomized phase II study of sequential carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) and gefitinib (G) in chemotherapy‐naive patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Preliminary results. Journal of Clinical Oncology: ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2006;24(18 Suppl):7096.
-
- Nokihara H, Ohe Y, Yamada K, et al. Randomized phase II study of sequential carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) and gefitinib (G) in chemotherapy‐naive patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC): final results [abstract no. 8069]. Journal of Clinical Oncology: ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2008;26(15 Suppl Pt I):441.
Puri 2013 {published data only}
-
- Puri T, Orlando M, Barraclough H, Enatsu S. A randomized phase 2 trial of pemetrexed (P) and gefitinib (G) versus g as first‐line treatment for patients with stage IV non‐squamous (NS) non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer Sydney, NSW Australia. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2013; Vol. 8:S1156‐7.
Additional references
ACS 2018
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2018. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer‐non‐smallcell/ (accessed 11th Jan 2018).
Bell 2005
-
- Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Maserlat SM, Harris PL, Okimoto FA, Brannigan BW, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non‐small‐cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(31):8081‐92. - PubMed
Boye 2016
-
- Boye M, Wang X, Srimuninnimit V, Kang JH, Tsai CM, Orlando M, et al. First‐line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance therapy versus gefitinib monotherapy in east Asian never‐smoker patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non‐small cell lung cancer: quality of life results from a randomized phase III trial. Clinical Lung Cancer 2016;17(2):150‐60. - PubMed
Cella 1995
-
- Cella D, Bonomi AE, Lloyd SR, Tulsky DS, Kaplan E, Bonomi P. Reliability and validity of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy ‐ Lung (FACT‐L) quality of life instrument. Lung Cancer 1995;12:199‐220. - PubMed
Cella 2002
-
- Cella D, Eton DT, Fairclough DL, Bonomi P, Heyes AE, Silberman C, et al. What is a clinically meaningful change on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy‐Lung (FACT‐L) Questionnaire? Results from Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Study 5592. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2002;55:285‐95. - PubMed
Cella 2005
-
- Cella D, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, et al. Clinically meaningful improvement in symptoms and quality of life for patients with non‐small cell lung cancer receiving gefitinib in a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(13):2946‐54. - PubMed
Chang 2006
-
- Chang A, Parikh P, Thongprasert S, Tan EH, Perng RP, Ganzon D, et al. Gefitinib (IRESSA) in patients of Asian origin with refractory advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer: Subset analysis from the ISEL study. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2006;1(8):847‐55. - PubMed
Douillard 2010
-
- Douillard JY, Shephard FA, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, et al. Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib and docetaxel in previously treated non‐small‐cell lung cancer: from the randomized phase III INTEREST trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(5):744‐52. - PubMed
Fukuoka 2011
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open‐label, first‐line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non ‐ small‐cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). Journal of Clinical Oncology. United States: American Society of Clinical Oncology (330 John Carlyle Street, Suite 300, Alexandria VA 22314, United States), 2011; Vol. 29:2866‐74. - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Herbst 2005
-
- Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, Fenrenbacher L, Johnson BE, Sandler A, et al. TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI‐774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(25):5892‐9. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. [www.cochrane‐handbook.org]
Hirsch 2006
-
- Hirsch FR, Varella‐Garcia M, Bunn Jr PA, Franklin WA, Dziadziuszko R, Thatcher N, et al. Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib in a phase III placebo‐controlled study in advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006;24(31):5034‐42. - PubMed
Ibrahim 2010
Inoue 2013
-
- Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib with carboplatin‐paclitaxel for chemo‐naive non‐small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations (NEJ002). Annals of Oncology 2013;24:54‐9. - PubMed
Jiang 2011
-
- Jiang J, Huang L, Liang X, Zhou X, Huang R, Chu Z, et al. Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Oncologica 2011;50(4):582‐8. - PubMed
Kosaka 2004
-
- Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Research 2004;64:8919‐23. - PubMed
Mok 2011
-
- Mok TSK. Personalized medicine in lung cancer: what we need to know. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology 2011;8:661‐8. - PubMed
NCI CTCAE 2010
-
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Common terminology criteria for adverse events. Common toxicity criteria, version 4.0. https://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_4.03_2010‐06‐14_QuickReference_... (accessed 17 February 2017).
Oizumi 2012
-
- Oizumi S, Kobayashi K, Inoue A, Maemondo M, Sugawara S, Yoshizawa H, et al. Quality of life with gefitinib in patients with EGFR‐mutated non‐small cell lung cancer: quality of life analysis of north east Japan study group 002 trial. Oncologist. United States: AlphaMed Press (318 Blackwell St. Suite 260, Durham NC 27701‐2884, United States), 2012; Vol. 17:863‐70. - PMC - PubMed
Paez 2004
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004;304:1497‐500. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Sekine 2009
-
- Sekine I, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Yamamoto N, Tsuboi M, Nakagawa K, et al. Quality of life and disease‐related symptoms in previously treated Japanese patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer: results of a randomized phase III study (V‐15‐32) of gefitinib versus docetaxel. Annals of Oncology 2009;20(9):1483‐8. - PubMed
Smith 2005
-
- Smith J. Erlotinib: small molecule targeted therapy in the treatment of non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Clinical Therapeutics 2005;27(10):1513‐34. - PubMed
Therasse 2000
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2000;92(3):205‐16. - PubMed
Thongprasert 2011
-
- Thongprasert S, Duffield E, Saijo N, Wu YL, Yang JC, Chu DT, et al. Health‐related quality‐of‐life in a randomized phase III first‐line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients from Asia with advanced NSCLC (IPASS). Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2011;6:1872‐80. - PubMed
Yamamoto 2010
-
- Yamamoto N, Nishiwaki Y, Negoro S, Jiang H, Itoh Y, Saijo N, et al. Disease control as a predictor of survival with gefitinib and docetaxel in a phase III study (V‐15‐32) in advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer patients. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2010;5(7):1042‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

