Successful resolution with apixaban of a massive left atrial appendage thrombus due to nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation: A case report and review
- PMID: 29336400
- PMCID: PMC5791497
- DOI: 10.4103/aca.ACA_146_17
Successful resolution with apixaban of a massive left atrial appendage thrombus due to nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation: A case report and review
Abstract
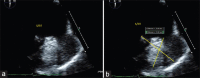
A 32-year-old woman with a past medical history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, long QT syndrome, and implantation of an automatic iimplantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) following cardiac arrest presented with disabling symptoms of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation due to recurrent AICD shocks. Before curative ablation, transesophageal echocardiography was performed to assess for existing thrombi. This is a rare case of successful resolution with apixaban of a massive left atrial appendage thrombus due to non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation that was successfully treated with apixaban.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham study. Stroke. 1991;22:983–8. - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC, Jr, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:e1–76. - PubMed
-
- Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous