Engineering the Surface of Therapeutic "Living" Cells
- PMID: 29336552
- PMCID: PMC8243527
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00157
Engineering the Surface of Therapeutic "Living" Cells
Abstract
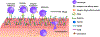
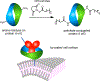
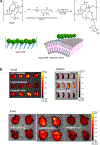
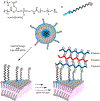
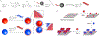
Biological cells are complex living machines that have garnered significant attention for their potential to serve as a new generation of therapeutic and delivery agents. Because of their secretion, differentiation, and homing activities, therapeutic cells have tremendous potential to treat or even cure various diseases and injuries that have defied conventional therapeutic strategies. Therapeutic cells can be systemically or locally transplanted. In addition, with their ability to express receptors that bind specific tissue markers, cells are being studied as nano- or microsized drug carriers capable of targeted transport. Depending on the therapeutic targets, these cells may be clustered to promote intercellular adhesion. Despite some impressive results with preclinical studies, there remain several obstacles to their broader development, such as a limited ability to control their transport, engraftment, secretion and to track them in vivo. Additionally, creating a particular spatial organization of therapeutic cells remains difficult. Efforts have recently emerged to resolve these challenges by engineering cell surfaces with a myriad of bioactive molecules, nanoparticles, and microparticles that, in turn, improve the therapeutic efficacy of cells. This review article assesses the various technologies developed to engineer the cell surfaces. The review ends with future considerations that should be taken into account to further advance the quality of cell surface engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




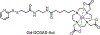





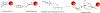

References
-
- Yee C; Thompson JA; Byrd D; Riddell SR; Roche P; Celis E; Greenberg PD Adoptive T Cell Therapy Using Antigen-Specific Cd8(+) T Cell Clones for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Melanoma: In Vivo Persistence, Migration, and Antitumor Effect of Transferred T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2002, 99, 16168–16173. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hussain MA; Theise ND Stem-Cell Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus. Lancet 2004, 364, 203–205. - PubMed
-
- Lagasse E; Connors H; Al-Dhalimy M; Reitsma M; Dohse M; Osborne L; Wang X; Finegold M; Weissman IL; Grompe M Purified Hematopoietic Stem Cells Can Differentiate into Hepatocytes in Vivo. Nat. Med 2000, 6, 1229–1234. - PubMed
-
- Nathan S; De SD; Thambyah A; Fen C; Goh J; Lee EH Cell-Based Therapy in the Repair of Osteochondral Defects: A Novel Use for Adipose Tissue. Tissue Eng 2003, 9, 733–744. - PubMed
-
- Buzhor E; Leshansky L; Blumenthal J; Barash H; Warshawsky D; Mazor Y; Shtrichman R Cell-Based Therapy Approaches: The Hope for Incurable Diseases. Regener. Med 2014, 9, 649–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

