Challenges and Opportunities for the Subcutaneous Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins
- PMID: 29336981
- PMCID: PMC5915922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2018.01.007
Challenges and Opportunities for the Subcutaneous Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins
Abstract
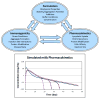
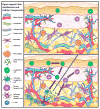
Biotherapeutics is a rapidly growing drug class, and over 200 biotherapeutics have already obtained approval, with about 50 of these being approved in 2015 and 2016 alone. Several hundred protein therapeutic products are still in the pipeline, including interesting new approaches to treatment. Owing to patients' convenience of at home administration and reduced number of hospital visits as well as the reduction in treatment costs, subcutaneous (SC) administration of biologics is of increasing interest. Although several avenues for treatment using biotherapeutics are being explored, there is still a sufficient gap in knowledge regarding the interplay of formulation conditions, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of the absorption of these compounds when they are given SC. This review seeks to highlight the major concerns and important factors governing this route of administration and suggest a holistic approach for effective SC delivery.
Keywords: absorption; bioavailability; biotechnology; formulation; immune response; pharmacokinetics; physicochemical properties; proteins.
Copyright © 2018 American Pharmacists Association®. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
References
-
- Biopharma. BIOPHARMA: Biopharmaceutical Products in the U.S. and European Markets U.S. Approvals, 2002-present. 2017.
-
- Rule S, Collins GP, Samanta K. Subcutaneous vs intravenous rituximab in patients with non- Hodgkin lymphoma: a time and motion study in the United Kingdom. Journal of medical economics. 2014;17(7):459–468. - PubMed
-
- Sanford M. Subcutaneous trastuzumab: a review of its use in HER2-positive breast cancer. Targeted oncology. 2014;9(1):85–94. - PubMed
-
- Ashai NI, Paganini EP, Wilson JM. Intravenous versus subcutaneous dosing of epoetin: a review of the literature. American journal of kidney diseases : the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 1993;22(2 Suppl 1):23–31. - PubMed
Table References
-
- Food and Drug Administration Approval Information. Adalimumab Product Approval Information – Licensing Action 12/31/02. 2002
-
- Food and Drug Administration Approval Information. Infliximab Product Approval Information - Licensing Action 11/10/99. 1999
-
- Food and Drug Administration Approval Information. RITUXAN HYCELA™ (rituximab and hyaluronidase human) injection, for subcutaneous use. 2017
-
- Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Schechtman J, Szczepanski L, Kavanaugh A, Racewicz AJ, van Vollenhoven RF, Li NF, Agarwal S, Hessey EW, Shaw TM. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2006;54(5):1390–1400. - PubMed
-
- Denoel A, Dieude P, Chollet-Martin S, Grootenboer-Mignot S. SAT0181 Immunogenicity of Rituximab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Kinetic Analysis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2015;74(Suppl 2):720–720.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous