Abrogation of Fam20c altered cell behaviors and BMP signaling of immortalized dental mesenchymal cells
- PMID: 29337188
- PMCID: PMC5866767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.01.004
Abrogation of Fam20c altered cell behaviors and BMP signaling of immortalized dental mesenchymal cells
Abstract
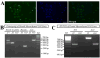
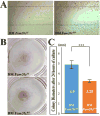
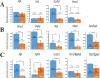
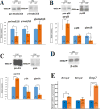
FAM20C mutations compromise the mineralization of skeleton and tooth in both human and mouse. Putatively, the mineralization disorder is attributed to the elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), which reduced the serum phosphorus by suppressing the reabsorption of phosphorus in kidney. Besides the regulation on systemic phosphorus homeostasis, FAM20C was also implicated to regulate cell behaviors and gene expression through a cell-autonomous manner. To identify the primary effects of Fam20c on dental mesenchymal cells, mouse Fam20c-deficient dental mesenchymal cells were generated by removing the floxed alleles from the immortalized mouse Fam20cf/f dental mesenchymal cells with Cre-expressing lentivirus. The removal of Fam20c exerted no impact on cell morphology, but suppressed the proliferation and mobility of the dental mesenchymal cells. Fam20c deficiency also significantly reduced the expression of Osterix, Runx2, type I Collagen a 1 (Col1a1), Alkaline phosphatase (Alpl) and the members of the small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoprotein (SIBLING) family, but increased Fgf23 expression. Consistently, the in vitro mineralization of Fam20c-deficient dental mesenchymal cells was severely disabled. However, supplements of the non-collagenous proteins from wild type rat dentin failed to rescue the compromised mineralization, suggesting that the roles of FAM20C in tooth mineralization are more than phosphorylating local matrices and regulating systemic phosphorus metabolism. Moreover, the down-regulated BMP signaling pathways in the Fam20c deficient dental mesenchymal cells revealed that the kinase activity of FAM20C might be required to maintain BMP signaling. In summary, our study discloses that Fam20c indeed regulates cell behaviors and cell signaling pathway in a cell-autonomous manner.
Keywords: Extracellular matrix; FAM20C; Mineralization; Phosphorylation; Secretory proteins.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FAM20C regulates osteoblast behaviors and intracellular signaling pathways in a cell-autonomous manner.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Apr;233(4):3476-3486. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26200. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28926103 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalized Mouse Floxed Fam20c Dental Papillar Mesenchymal and Osteoblast Cell Lines Retain Their Primary Characteristics.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Nov;230(11):2581-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25008. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25833681 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of a novel FGF23 regulator, FAM20C, leads to hypophosphatemic rickets in mice.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(5):e1002708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002708. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22615579 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation potential of dental papilla, dental pulp, and apical papilla progenitor cells.J Endod. 2010 May;36(5):781-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.02.006. Epub 2010 Mar 24. J Endod. 2010. PMID: 20416419 Review.
-
The ABCs of the atypical Fam20 secretory pathway kinases.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100267. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100267. Epub 2021 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33759783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inactivation of FAM20B causes cell fate changes in annulus fibrosus of mouse intervertebral disc and disc defects via the alterations of TGF-β and MAPK signaling pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Dec 1;1865(12):165555. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165555. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 31513834 Free PMC article.
-
Fam20C overexpression in odontoblasts regulates dentin formation and odontoblast differentiation.J Mol Histol. 2023 Aug;54(4):329-347. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10123-y. Epub 2023 Jun 26. J Mol Histol. 2023. PMID: 37357253
-
The odontoblastic differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells: molecular regulation mechanism and related genetic syndromes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 25;11:1174579. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1174579. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37818127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ablation of FAM20C caused short root defects via suppressing the BMP signaling pathway in mice.J Orofac Orthop. 2023 Nov;84(6):349-361. doi: 10.1007/s00056-022-00386-7. Epub 2022 Mar 22. J Orofac Orthop. 2023. PMID: 35316352 English.
-
Mutations that prevent phosphorylation of the BMP4 prodomain impair proteolytic maturation of homodimers leading to lethality in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 1:2024.10.08.617306. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.08.617306. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 May 29;14:RP105018. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105018. PMID: 39416136 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hao J, Narayanan K, Muni T, Ramachandran A, George A. Dentin matrix protein 4, a novel secretory calcium-binding protein that modulates odontoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(21):15357–15365. - PubMed
-
- Simpson MA, Hsu R, Keir LS, Hao J, Sivapalan G, Ernst LM, Zackai EH, Al-Gazali LI, Hulskamp G, Kingston HM, Prescott TE, Ion A, Patton MA, Murday V,George A, Crosby AH. Mutations in FAM20C are associated with lethal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia (Raine syndrome), highlighting a crucial molecule in bone development. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81(5):906–912. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simpson MA1, Scheuerle A, Hurst J, Patton MA, Stewart H, Crosby AH. Mutations in FAM20C also identified in non-lethal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia. Clin Genet. 2009;75(3):271–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

